High resolution manometry and multichannel intraluminal impedance oesophageal manometry in clinical practice
- PMID: 28839558
- PMCID: PMC5536775
- DOI: 10.1136/fg.2009.000620
High resolution manometry and multichannel intraluminal impedance oesophageal manometry in clinical practice
Abstract
The past decade has seen new technological advances in the investigation of oesophageal motility disorders. Multichannel intraluminal impedance monitoring has been used as an adjunct to conventional manometry in the assessment of oesophageal function, independent of radiography. High resolution manometry provides additional information over conventional manometry, and its topographic analysis makes interpretation of studies easier. Both utilities in non-obstructive dysphagia have been used ultimately in research; however, more studies are addressing their clinical application.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Figures
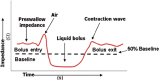
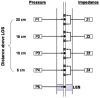
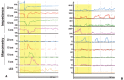
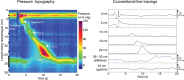
References
-
- Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: clinical use of esophageal manometry. Gastroenterology 2005;128:207–8. - PubMed
-
- Massey BT, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ, et al. Abnormal esophageal motility. An analysis of concurrent radiographic and manometric findings. Gastroenterology 1991;101:344–54. - PubMed
-
- Silny J. Intraluminal multiple electric impedance procedure for measurement of gastrointestinal motility. J Gastrointest Motil 1991;3:151–62.
-
- Silny J, Knigge KP, Fass J, et al. Verification of the intraluminal multiple electrical impedance measurement for the recording of gastrointestinal motility. J Gastrointest Motil 1993;5:107–22.
-
- Imam H, Shay S, Ali A, et al. Bolus transit patterns in healthy subjects: a study using simultaneous impedance monitoring, videoesophagram, and esophageal manometry. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2005;288:G1000–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
