Why an extended evolutionary synthesis is necessary
- PMID: 28839929
- PMCID: PMC5566817
- DOI: 10.1098/rsfs.2017.0015
Why an extended evolutionary synthesis is necessary
Erratum in
-
Correction to 'Why an extended evolutionary synthesis is necessary'.Interface Focus. 2017 Dec 6;7(6):20170065. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2017.0065. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Interface Focus. 2017. PMID: 29147560 Free PMC article.
Abstract
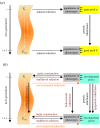
Since the last major theoretical integration in evolutionary biology-the modern synthesis (MS) of the 1940s-the biosciences have made significant advances. The rise of molecular biology and evolutionary developmental biology, the recognition of ecological development, niche construction and multiple inheritance systems, the '-omics' revolution and the science of systems biology, among other developments, have provided a wealth of new knowledge about the factors responsible for evolutionary change. Some of these results are in agreement with the standard theory and others reveal different properties of the evolutionary process. A renewed and extended theoretical synthesis, advocated by several authors in this issue, aims to unite pertinent concepts that emerge from the novel fields with elements of the standard theory. The resulting theoretical framework differs from the latter in its core logic and predictive capacities. Whereas the MS theory and its various amendments concentrate on genetic and adaptive variation in populations, the extended framework emphasizes the role of constructive processes, ecological interactions and systems dynamics in the evolution of organismal complexity as well as its social and cultural conditions. Single-level and unilinear causation is replaced by multilevel and reciprocal causation. Among other consequences, the extended framework overcomes many of the limitations of traditional gene-centric explanation and entails a revised understanding of the role of natural selection in the evolutionary process. All these features stimulate research into new areas of evolutionary biology.
Keywords: evolutionary biology; evolutionary developmental biology; extended synthesis; modern synthesis; niche construction; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
I declare I have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The extended evolutionary synthesis: its structure, assumptions and predictions.Proc Biol Sci. 2015 Aug 22;282(1813):20151019. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.1019. Proc Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26246559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On Reciprocal Causation in the Evolutionary Process.Evol Biol. 2018;45(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s11692-017-9431-x. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Evol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29497217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why evolutionary biology needs anthropology: Evaluating core assumptions of the extended evolutionary synthesis.Evol Anthropol. 2018 Nov;27(6):267-284. doi: 10.1002/evan.21747. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Evol Anthropol. 2018. PMID: 30444563 Review.
-
Domestication as a model system for the extended evolutionary synthesis.Interface Focus. 2017 Oct 6;7(5):20160133. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2016.0133. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Interface Focus. 2017. PMID: 28839915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extended evolutionary synthesis and human origins: Archaeological perspectives.Evol Anthropol. 2021 Jan;30(1):4-7. doi: 10.1002/evan.21837. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Evol Anthropol. 2021. PMID: 32574411
Cited by
-
Evolution and sustainability: gathering the strands for an Anthropocene synthesis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Jan;379(1893):20220251. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0251. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 37952619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health, consciousness, and the evolution of subjects.Synthese. 2023;201(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s11229-022-03998-z. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Synthese. 2023. PMID: 36570034 Free PMC article.
-
An evolutionary process without variation and selection.J R Soc Interface. 2021 Jul;18(180):20210334. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2021.0334. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J R Soc Interface. 2021. PMID: 34314653 Free PMC article.
-
Why did the human brain size evolve? A way forward.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;380(1929):20240114. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0114. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40566920 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of prenatal glucocorticoids and thyroid hormones on developmental plasticity of mitochondrial aerobic metabolism, growth and survival: an experimental test in wild great tits.J Exp Biol. 2022 May 1;225(9):jeb243414. doi: 10.1242/jeb.243414. Epub 2022 May 10. J Exp Biol. 2022. PMID: 35420125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Einstein A. 1916. Ernst Mach. Physikalische Zeitschrift 17, 101–104.
-
- Jablonka E, Lamb MJ. 2006. Evolution in four dimensions. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

