Effect of Huisheng oral solution on coagulation function in perioperative period in patients with primary lung cancer
- PMID: 28839987
- PMCID: PMC5542976
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.06.64
Effect of Huisheng oral solution on coagulation function in perioperative period in patients with primary lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is about 4-10% in lung cancer patients. Huisheng oral solution (HSOS) has been previously demonstrated to inhibit carageenan induced acute thrombosis in rats, reduce the incidence of thrombosis in the lungs and mesentery of tumor-bearing mice and inhibit tumor cell metastasis. The purpose of this study was to assess the anticoagulant effect of HSOS in lung cancer patients in the perioperative period.
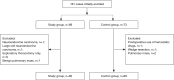
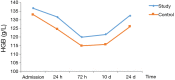
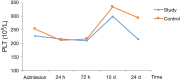
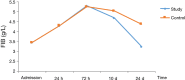
Methods: This study was a multicenter, randomized, single-blind, blank-controlled clinical trial. A total of patients at five hospitals in Hebei Province, China were included. The patients were randomly divided into study group or control group according to random number table. The primary outcome was the blood test indices in both groups. The study group was given oral HSOS (20 mL, bid) from admission until 24 h before surgery. If no active bleeding was observed, the patients were given oral HSOS (20 mL, tid) from 24 h to 24 d postoperatively. The patients in the study group did not receive any other anticoagulation therapy during the study period and the control group only underwent surgery. The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee of principal investigator hospital. Blood samples were taken at admission (before therapy), 24 h, 72 h, 10 d (before discharge) and 24 d (first visit after discharge) after surgery. Routine blood tests [red blood cell (RBC) count, white blood cell (WBC) count, hemoglobin (HGB), and platelet (PLT) count] and coagulation function test [prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), fibrinogen (FIB), and plasma D-dimer] were performed. The changes in outcome measures over time were analyzed by repeated measures analysis of variance to compare the differences between groups and between different time points and assess the impact of tumor stage and mode of surgery on them. All tests were two-tailed, and P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: The results differed between different tumor stage groups. In stage III-IV group, there was no significant difference in various indices between the study group and control group. In stage I-II group, there was significant difference in hemoglobin (P=0.004), platelet count (P=0.007), fibrinogen (P=0.046), and plasma D-dimer (24 d: P=0.032) between two groups. Fibrinogen reach the peak 72 h after surgery, and other indices reach the peak 7-10 d postoperatively and declined one month after surgery, and the decline tendency was different between two groups. In addition, no adverse drug reaction was observed in both the study group and control group.
Conclusions: HSOS (20 mL, tid) is of good safety profile and does not increase the risk of bleeding. With its unique characteristic of convenience for being taken, HSOS (20 mL, tid) could be a proper treatment for lung cancer patients in the perioperative period.
Keywords: Huisheng oral solution (HSOS); coagulation function; primary lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- The Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Third national retrospect spot-check of death-causation. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
