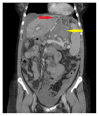
Hemoperitoneum Secondary to Spontaneous Rupture of a Retroperitoneal Varix
- PMID: 28840045
- PMCID: PMC5559919
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1829676
Hemoperitoneum Secondary to Spontaneous Rupture of a Retroperitoneal Varix
Abstract
Hemoperitoneum due to a ruptured retroperitoneal varix is an exceedingly rare condition and a poor prognostic sign with catastrophic and life-threatening complication of portal hypertension. We present a unique case of a 56-year-old female with cirrhosis secondary to primary sclerosing cholangitis who presented with acute abdominal pain and hypovolemic shock prior to a cardiac arrest following a ruptured retroperitoneal varix without prior esophageal varices and a newly identified intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. The clinical presentation with abdominal pain and hemorrhagic shock is consistently reported in the relevant literature. Early recognition affords appropriate management and urgent surgical intervention leading to survival.
Figures
References
-
- Lyon D. T., Mantia A. G., Schubert T. T. Hemoperitoneum from a ruptured varix in cirrhosis. Case report and literature review. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 1979;71(6):611–616. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources