Retrospective on Cholesterol Homeostasis: The Central Role of Scap
- PMID: 28841344
- PMCID: PMC5828883
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-011852
Retrospective on Cholesterol Homeostasis: The Central Role of Scap
Abstract
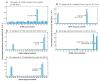
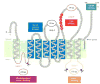
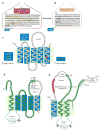
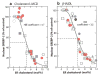
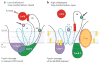
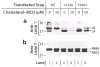
Scap is a polytopic membrane protein that functions as a molecular machine to control the cholesterol content of membranes in mammalian cells. In the 21 years since our laboratory discovered Scap, we have learned how it binds sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) and transports them from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi for proteolytic processing. Proteolysis releases the SREBP transcription factor domains, which enter the nucleus to promote cholesterol synthesis and uptake. When cholesterol in ER membranes exceeds a threshold, the sterol binds to Scap, triggering several conformational changes that prevent the Scap-SREBP complex from leaving the ER. As a result, SREBPs are no longer processed, cholesterol synthesis and uptake are repressed, and cholesterol homeostasis is restored. This review focuses on the four domains of Scap that undergo concerted conformational changes in response to cholesterol binding. The data provide a molecular mechanism for the control of lipids in cell membranes.
Keywords: COPII vesicles; ER-to-Golgi transport; Insig; SREBPs; Scap; cholesterol; conformational changes; membrane proteins; proteolytic processing; transcriptional regulation.
Figures


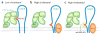
References
-
- Hua X, Nohturfft A, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Sterol resistance in CHO cells traced to point mutation in SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP) Cell. 1996;87:415–26. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

