ESRRA (estrogen-related receptor α) is a key coordinator of transcriptional and post-translational activation of autophagy to promote innate host defense
- PMID: 28841353
- PMCID: PMC5846564
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1339001
ESRRA (estrogen-related receptor α) is a key coordinator of transcriptional and post-translational activation of autophagy to promote innate host defense
Abstract
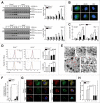
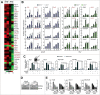
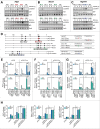
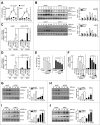
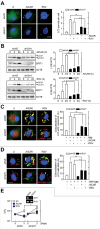
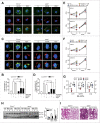
The orphan nuclear receptor ESRRA (estrogen-related receptor α) is a key regulator of energy homeostasis and mitochondrial function. Macroautophagy/autophagy, an intracellular degradation process, is a critical innate effector against intracellular microbes. Here, we demonstrate that ESRRA is required for the activation of autophagy to promote innate antimicrobial defense against mycobacterial infection. AMP-activated protein kinase pathway and SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) activation led to induction of ESRRA, which is essential for autophagosome formation, in bone marrow-derived macrophages. ESRRA enhanced the transcriptional activation of numerous autophagy-related (Atg) genes containing ERR response elements in their promoter regions. Furthermore, ESRRA, operating in a feed-forward loop with SIRT1, was required for autophagy activation through deacetylation of ATG5, BECN1, and ATG7. Importantly, ESRRA deficiency resulted in a decrease of phagosomal maturation and antimicrobial responses against mycobacterial infection. Thus, we identify ESRRA as a critical activator of autophagy via both transcriptional and post-translational control to promote antimicrobial host responses.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; autophagy-related genes; estrogen-related receptor α; innate antimicrobial defense; post-translational modifications; sirtuin 1.
Figures

References
-
- Evans RM, Mangelsdorf DJ. Nuclear receptors, RXR, and the Big Bang. Cell 2014; 157:255-66; PMID:24679540; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giguère V, Yang N, Segui P, Evans RM. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature 1988; 331:91-4; PMID:3267207; https://doi.org/10.1038/331091a0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deblois G, Giguère V. Functional and physiological genomics of estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011; 1812:1032-40; PMID:21172432; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.12.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Villena JA, Kralli A. ERRalpha: a metabolic function for the oldest orphan. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2008; 19:269-76; PMID:18778951; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2008.07.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sonoda J, Laganière J, Mehl IR, Barish GD, Chong LW, Li X, Scheffler IE, Mock DC, Bataille AR, Robert F, et al.. Nuclear receptor ERR alpha and coactivator PGC-1 beta are effectors of IFN-gamma-induced host defense. Genes Dev 2007; 21:1909-20; PMID:17671090; https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1553007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
