Clonal Evolution of Autoreactive Germinal Centers
- PMID: 28841417
- PMCID: PMC5784431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.026
Clonal Evolution of Autoreactive Germinal Centers
Abstract
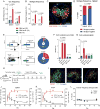
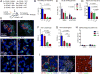
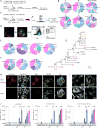
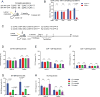
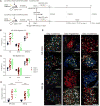
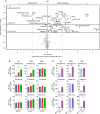
Germinal centers (GCs) are the primary sites of clonal B cell expansion and affinity maturation, directing the production of high-affinity antibodies. This response is a central driver of pathogenesis in autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but the natural history of autoreactive GCs remains unclear. Here, we present a novel mouse model where the presence of a single autoreactive B cell clone drives the TLR7-dependent activation, expansion, and differentiation of other autoreactive B cells in spontaneous GCs. Once tolerance was broken for one self-antigen, autoreactive GCs generated B cells targeting other self-antigens. GCs became independent of the initial clone and evolved toward dominance of individual clonal lineages, indicating affinity maturation. This process produced serum autoantibodies to a breadth of self-antigens, leading to antibody deposition in the kidneys. Our data provide insight into the maturation of the self-reactive B cell response, contextualizing the epitope spreading observed in autoimmune disease.
Keywords: B-lymphocytes; autoantibodies; autoantigens; autoimmune diseases; autoimmunity; autoreactive B cells; epitope spreading; germinal center; self-tolerance; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, James JA, Harley JB. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1526–1533. - PubMed
-
- Berland R, Fernandez L, Kari E, Han J-H, Lomakin I, Akira S, Wortis HH, Kearney JF, Ucci AA, Imanishi-Kari T. Toll-like receptor 7-dependent loss of B cell tolerance in pathogenic autoantibody knockin mice. Immunity. 2006;25:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Busse CE, Czogiel I, Braun P, Arndt PF, Wardemann H. Single-cell based high-throughput sequencing of full-length immunoglobulin heavy and light chain genes. Eur J Immunol. 2013;44:597–603. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

