Pre-treatment with Lactobacillus plantarum prevents severe pathogenesis in mice infected with Leptospira interrogans and may be associated with recruitment of myeloid cells
- PMID: 28841659
- PMCID: PMC5589268
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005870
Pre-treatment with Lactobacillus plantarum prevents severe pathogenesis in mice infected with Leptospira interrogans and may be associated with recruitment of myeloid cells
Abstract
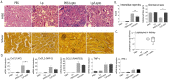
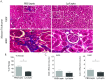
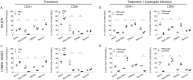
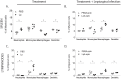
Recent estimates on global morbidity and mortality caused by Leptospirosis point to one million cases and almost 60,000 deaths a year worldwide, especially in resource poor countries. We analyzed how a commensal probiotic immunomodulator, Lactobacillus plantarum, affects Leptospira interrogans pathogenesis in a murine model of sub-lethal leptospirosis. We found that repeated oral pre-treatment of mice with live L. plantarum restored body weight to normal levels in mice infected with L. interrogans. Pre-treatment did not prevent L. interrogans access to the kidney but it affected the inflammatory response and it reduced histopathological signs of disease. Analysis of the immune cell profiles in lymphoid tissues of mice pre-treated with L. plantarum showed increased numbers of B cells as well as naïve and memory CD4+ helper T cell populations in uninfected mice that shifted towards increased numbers of effector CD4+ helper T in infected mice. CD8+ cytotoxic T cell profiles in pre-treated uninfected and infected mice mirrored the switch observed for CD4+ except that CD8+ memory T cells were not affected. In addition, pre-treatment led to increased populations of monocytes in lymphoid tissues of uninfected mice and to increased populations of macrophages in the same tissues of infected mice. Immunohistochemistry of kidney sections of pre-treated infected mice showed an enrichment of neutrophils and macrophages and a reduction of total leucocytes and T cells. Our results suggest that complex myeloid and T cell responses orchestrate the deployment of monocytes and other cells from lymphoid tissue and the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages to the kidney, and that, the presence of these cells in the target organ may be associated with reductions in pathogenesis observed in infected mice treated with L. plantarum.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and some of the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests. HHP, LR and MGS are or were employed in part by a commercial company, Immuno Technologies, Inc. We thank the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases for funding support (R44 AI096551) to MGS via Immuno Technologies, Inc. The funder provided support in the form of salaries for authors [HHP, LR, MGS], but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ section. MGS holds more than 5% financial interest in Immuno Technologies, Inc. and LR holds 5% financial interest in Immuno Technologies Inc. CW declares no conflicts.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Leptospira Interrogans induces fibrosis in the mouse kidney through Inos-dependent, TLR- and NLR-independent signaling pathways.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jan 30;8(1):e2664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002664. eCollection 2014. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24498450 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse model for sublethal Leptospira interrogans infection.Infect Immun. 2015 Dec;83(12):4693-700. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01115-15. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26416909 Free PMC article.
-
Myocarditis and neutrophil-mediated vascular leakage but not cytokine storm associated with fatal murine leptospirosis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Feb;112:105571. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105571. Epub 2025 Jan 30. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39889371 Free PMC article.
-
Recent findings related to immune responses against leptospirosis and novel strategies to prevent infection.Microbes Infect. 2018 Oct-Nov;20(9-10):578-588. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Microbes Infect. 2018. PMID: 29452258 Review.
-
Current treatment options for leptospirosis: a mini-review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 25;15:1403765. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1403765. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38725681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Immunomodulatory Effects and Applications of Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum in Vaccine Development.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Dec;16(6):2229-2250. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10338-9. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39101975 Review.
-
Repurposing Disulfiram (Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide) as a Potential Drug Candidate against Borrelia burgdorferi In Vitro and In Vivo.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Sep 22;9(9):633. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090633. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32971817 Free PMC article.
-
Phagocyte Escape of Leptospira: The Role of TLRs and NLRs.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 6;11:571816. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.571816. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33123147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus plantarum prevents and mitigates alcohol-induced disruption of colonic epithelial tight junctions, endotoxemia, and liver damage by an EGF receptor-dependent mechanism.FASEB J. 2018 Jun 18;32(11):fj201800351R. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800351R. Online ahead of print. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29912589 Free PMC article.
-
A Mouse Model of Sublethal Leptospirosis: Protocols for Infection with Leptospira Through Natural Transmission Routes, for Monitoring Clinical and Molecular Scores of Disease, and for Evaluation of the Host Immune Response.Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2020 Dec;59(1):e127. doi: 10.1002/cpmc.127. Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33141517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costa F, Hagan JE, Calcagno J, Kane M, Torgerson P, Martinez-Silveira MS, et al. Global morbidity and mortality of leptospirosis: a systematic review. Plos negl trop dis. 2015;9(9):e0003898 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003898 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, et al. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. The lancet infectious diseases. 2003;3(12):757–71. . - PubMed
-
- Haake DA, Levett PN. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr top microbiol immunol. 2015;387:65–97. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-45059-8_5 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levett PN. Leptospirosis. Clin microbiol rev. 2001;14(2):296–326. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.2.296-326.2001 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cumberland P, Everard CO, Levett PN. Assessment of the efficacy of an igm-elisa and microscopic agglutination test (mat) in the diagnosis of acute leptospirosis. Am j trop med hyg. 1999;61(5):731–4. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

