Review: Metabolic Control of Immune System Activation in Rheumatic Diseases
- PMID: 28841779
- PMCID: PMC5711528
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40223
Review: Metabolic Control of Immune System Activation in Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
Metabolic pathways mediate lineage specification within the immune system through the regulation of glucose utilization, a process that generates energy in the form of ATP and synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, and lipids to enable cell growth, proliferation, and survival. CD4+ T cells, a proinflammatory cell subset, preferentially produce ATP through glycolysis, whereas cells with an antiinflammatory lineage, such as memory and regulatory T cells, favor mitochondrial ATP generation. In conditions of metabolic stress or a shortage of nutrients, cells rely on autophagy to secure amino acids and other substrates, while survival depends on the sparing of mitochondria and maintenance of a reducing environment. The pentose phosphate pathway acts as a key gatekeeper of inflammation by supplying ribose-5-phosphate for cell proliferation and NADPH for antioxidant defenses. Increased lysosomal catabolism, accumulation of branched amino acids, glutamine, kynurenine, and histidine, and depletion of glutathione and cysteine activate the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), an arbiter of lineage development within the innate and adaptive immune systems. Mapping the impact of susceptibility genes to metabolic pathways allows for better understanding and therapeutic targeting of disease-specific expansion of proinflammatory cells. Therapeutic approaches aimed at glutathione depletion and mTOR pathway activation appear to be safe and effective for treating lupus, while an opposing intervention may be of benefit in rheumatoid arthritis. Environmental sources of origin for metabolites within immune cells may include microbiota and plants. Thus, a better understanding of the pathways of immunometabolism could provide new insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of the rheumatic diseases.
© 2017 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
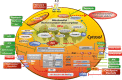

References
-
- Banki K, Hutter E, Colombo E, Gonchoroff NJ, Perl A. Glutathione levels and sensitivity to apoptosis are regulated by changes in transaldolase expression. J Biol Chem 1996;271:32994–3001. - PubMed
-
- Banki K, Hutter E, Gonchoroff NJ, Perl A. Molecular ordering in HIV‐induced apoptosis: oxidative stress, activation of caspases, and cell survival are regulated by transaldolase. J Biol Chem 1998;273:11944–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

