A systematic review of diagnostic methods to differentiate acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome from cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- PMID: 28841896
- PMCID: PMC6389074
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1809-8
A systematic review of diagnostic methods to differentiate acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome from cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Abstract
Background: Discriminating acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) from cardiogenic pulmonary edema (CPE) is often challenging. This systematic review examines studies using biomarkers or images to distinguish ALI/ARDS from CPE.
Methods: Three investigators independently identified studies designed to distinguish ALI/ARDS from CPE in adults. Studies were identified from PubMed, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials database until July 3, 2017.
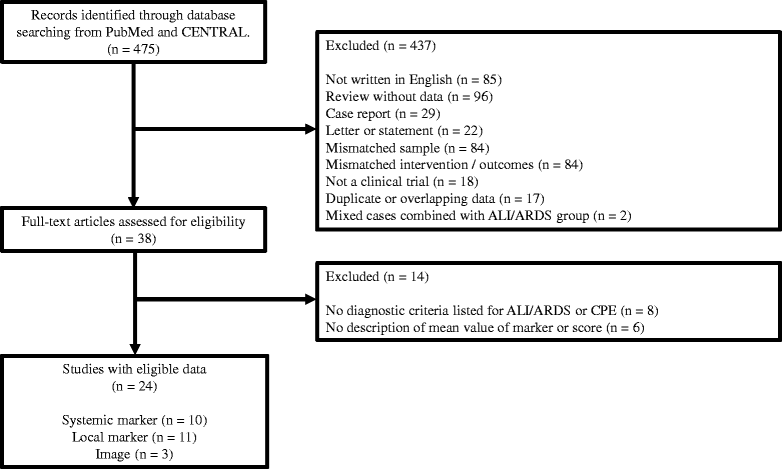
Results: Of 475 titles and abstracts screened, 38 full texts were selected for review, and we finally included 24 studies in this systematic review: 21 prospective observational studies, two retrospective observational studies, and one retrospective combined with prospective study. These studies compared various biomarkers to differentiate subjects with ALI/ARDS and in those with CPE, and 13 calculated the area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC). The most commonly studied biomarker (four studies) was brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and the discriminatory ability ranged from AUC 0.67-0.87 but the timing of measurement varied. Other potential biomarkers or tools have been reported, but only as single studies.
Conclusions: There were no identified biomarkers or tools with high-quality evidence for differentiating ALI/ARDS from CPE. Combining clinical criteria with validated biomarkers may improve the predictive accuracy.
Keywords: Acute respiratory failure; Biomarkers; Heart failure; Pulmonary edema.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable due to type of article with the exclusive use of previously published data for review article.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149(3 Pt 1):818–24. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.7509706. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Connors AF, Jr, Speroff T, Dawson NV, Thomas C, Harrell FE, Jr, Wagner D, Desbiens N, Goldman L, Wu AW, Califf RM, et al. The effectiveness of right heart catheterization in the initial care of critically ill patients. SUPPORT Investigators. JAMA. 1996;276(11):889–97. doi: 10.1001/jama.1996.03540110043030. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous