A comparison of radiographic and clinical outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody fusion performed with either a cellular bone allograft containing multipotent adult progenitor cells or recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2
- PMID: 28841904
- PMCID: PMC5574155
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-017-0618-8
A comparison of radiographic and clinical outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody fusion performed with either a cellular bone allograft containing multipotent adult progenitor cells or recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2
Abstract
Background: Both the map3 Cellular Allogeneic Bone Graft® and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (rhBMP-2, Infuse®) were developed to provide an alternative to iliac crest autograft, thus eliminating the morbidity associated with its harvest. The recent literature concerning adverse events associated with the use of rhBMP-2, however, highlights the need for a safe and effective alternative. The multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPC) found in map3 allograft may provide this alternative. The purpose of this study is to report 1-year outcomes of patients treated via anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) using either map3 Cellular Allogeneic Bone Graft or rhBMP-2 for bony fusion.
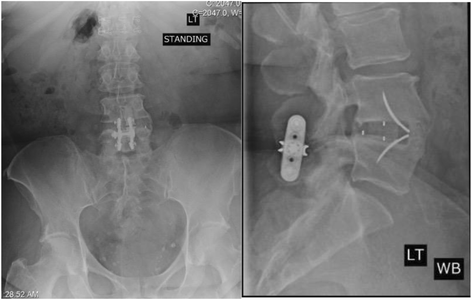
Methods: This was a retrospective evaluation of 41 patients treated via ALIF with either map3 or rhBMP-2 in a polyetheretherketone cage with posterior stabilization at 1, 2, or 3 consecutive levels (L3-S1). Patients were equally divided between treatment groups. The Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) and visual analog scores (VAS) for pain were documented as part of the standard of care. An independent radiologist assessed bridging of bone, disc height, and lordosis. Primary outcome measures included radiographic analysis of fusion by plain film and CTs. Secondary clinical outcomes included visual analogue scale for neck and arm pain and low back disability index scores.
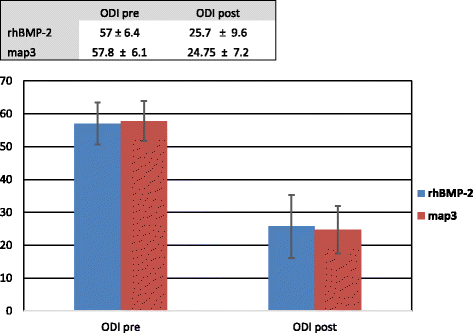
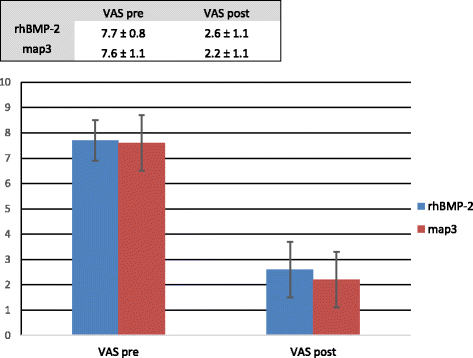
Results: The overall fusion rate was 91%, with no significant difference between groups. Improvements in ODI and VAS were observed among all patients (p < 0.001), with no significant difference between groups for ODI (p = 0.966) or VAS (p = 0.251). There was no significant difference in terms of changes to disc height and lordosis between groups (p < 0.05). The rhBMP-2 group had increased post-operative complications when compared to the map3 group, but the low numbers precluded statistical analysis.
Conclusion: Improvements in radiographic and clinical findings were observed in both treatment groups one-year postoperatively. Map3 allograft demonstrated equivalent fusion rates to rhBMP-2. A review of surgical supply costs at the treatment facility favored map3 allograft for the treatment of patients with DDD undergoing an ALIF in 1-3 levels compared to rhBMP-2. Further studies to evaluate long-term outcomes and post-operative complications are required.
Keywords: Cellular bone allograft; Lumbar spine fusion; MAPC; Map3; rhBMP-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Western Institutional Review Board approved this study (number 203609) and waived the requirement to obtain consent, as this was a purely retrospective study which followed standard of care.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Relevant activities outside the submitted work: DL has received payment for lecture from RTI Surgical.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Weiss AJ, Elixhauser A, Andrews RM. Trends in Operating Room Procedures in U.S. Hospitals, 2001—2011. Rockville, Maryland, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2014 [September 12, 2014]; Available from: http://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb170-Operating-Room-Procedur....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

