Oxidative stress and cellular pathways of asthma and inflammation: Therapeutic strategies and pharmacological targets
- PMID: 28842273
- PMCID: PMC5743757
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.08.011
Oxidative stress and cellular pathways of asthma and inflammation: Therapeutic strategies and pharmacological targets
Abstract
Asthma is a complex inflammatory disease characterized by airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. The mechanisms associated with the development and progression of asthma have been widely studied in multiple populations and animal models, and these have revealed involvement of various cell types and activation of intracellular signaling pathways that result in activation of inflammatory genes. Significant contributions of Toll-like-receptors (TLRs) and transcription factors such as NF-кB, have been reported as major contributors to inflammatory pathways. These have also recently been associated with mechanisms of oxidative biology. This is of important clinical significance as the observed inefficacy of current available treatments for severe asthma is widely attributed to oxidative stress. Therefore, targeting oxidizing molecules in conjunction with inflammatory mediators and transcription factors may present a novel therapeutic strategy for asthma. In this review, we summarize TLRs and NF-кB pathways in the context of exacerbation of asthma pathogenesis and oxidative biology, and we discuss the potential use of polyphenolic flavonoid compounds, known to target these pathways and possess antioxidant activity, as potential therapeutic agents for asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; Inflammation; NF-кB; Oxidative stress; Polyphenolic flavonoid compounds; Toll-like receptors.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
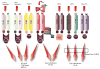
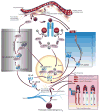
References
-
- Abel B, Thieblemont N, Quesniaux VJ, Brown N, Mpagi J, Miyake K, Bihl F, Ryffel B. Toll-like receptor 4 expression is required to control chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. J Immunol. 2002;169:3155–3162. - PubMed
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Akdis CA, Kussebi F, Pulendran B, Akdis M, Lauener RP, Schmidt-Weber CB, Klunker S, Isitmangil G, Hansjee N, Wynn TA, Dillon S, Erb P, Baschang G, Blaser K, Alkan SS. Inhibition of T helper 2-type responses, IgE production and eosinophilia by synthetic lipopeptides. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:2717–2726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

