Single-Center Experience Implementing the LOINC-RSNA Radiology Playbook for Adult Abdomen/Pelvis CT and MR Procedures Using a Semi-Automated Method
- PMID: 28842816
- PMCID: PMC5788822
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-017-0016-0
Single-Center Experience Implementing the LOINC-RSNA Radiology Playbook for Adult Abdomen/Pelvis CT and MR Procedures Using a Semi-Automated Method
Abstract
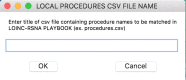
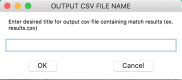
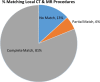
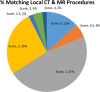
The LOINC-RSNA Radiology Playbook represents the future direction of standardization for radiology procedure names. We developed a software solution ("RadMatch") utilizing Python 2.7 and FuzzyWuzzy, an open-source fuzzy string matching algorithm created by SeatGeek, to implement the LOINC-RSNA Radiology Playbook for adult abdomen and pelvis CT and MR procedures performed at our institution. Execution of this semi-automated method resulted in the assignment of appropriate LOINC numbers to 86% of local CT procedures. For local MR procedures, appropriate LOINC numbers were assigned to 75% of these procedures whereas 12.5% of local MR procedures could only be partially mapped. For the standardized local procedures, only 63% of CT and 71% of MR procedures had corresponding RadLex Playbook identifier (RPID) codes in the LOINC-RSNA Radiology Playbook, which limited the utility of RPID codes. RadMatch is a semi-automated open-source software tool that can assist radiology departments seeking to standardize their radiology procedures via implementation of the LOINC-RSNA Radiology Playbook.
Keywords: LOINC; Playbook; Python; RSNA.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- RadLex Playbook. Radiological Society of North America. https://www.rsna.org/RadLex_Playbook.aspx. Accessed August 8, 2016.
-
- RSNA. LOINC from Regenstreif. https://loinc.org/collaboration/rsna. Accessed December 9, 2016.
-
- LOINC Users’ Guide. LOINC from Regenestreif. https://loinc.org/download/loinc-users-guide/. Accessed December 9, 2016.
-
- RELMA. LOINC from Regenestreif. https://loinc.org/relma/. Accessed July 20, 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

