The 3 Cs of Antibiotic Allergy-Classification, Cross-Reactivity, and Collaboration
- PMID: 28843343
- PMCID: PMC5681410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.06.017
The 3 Cs of Antibiotic Allergy-Classification, Cross-Reactivity, and Collaboration
Erratum in
-
Correction.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018 Jan-Feb;6(1):323. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.11.019. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018. PMID: 29310765 No abstract available.
-
Corrigendum.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Dec;10(12):3346-3347. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.10.001. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 36496222 No abstract available.
Abstract
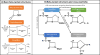
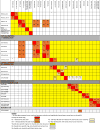
Antibiotic allergy labeling is highly prevalent and negatively impacts patient outcomes and antibiotic appropriateness. Reducing the prevalence and burden of antibiotic allergies requires the engagement of key stakeholders such as allergists, immunologists, pharmacists, and infectious diseases physicians. To help address this burden of antibiotic allergy overlabeling, we review 3 key antibiotic allergy domains: (1) antibiotic allergy classification, (2) antibiotic cross-reactivity, and (3) multidisciplinary collaboration. We review the available evidence and research gaps of currently used adverse drug reaction classification systems, antibiotic allergy cross-reactivity, and current and future models of antibiotic allergy care.
Keywords: Antibiotic allergy; Antimicrobial allergy; Cephalosporin allergy; Cross-reactivity; Penicillin allergy; Prevalence.
Copyright © 2017 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou L, Dhopeshwarkar N, Blumenthal KG, Goss F, Topaz M, Slight SP, et al. Drug Allergies Documented in Electronic Health Records of a Large Healthcare System. Allergy. 2016 - PubMed
-
- Charneski L, Deshpande G, Smith SW. Impact of an antimicrobial allergy label in the medical record on clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients. Pharmacotherapy. 2011;31:742–7. - PubMed
-
- Macy E, Contreras R. Health care use and serious infection prevalence associated with penicillin “allergy” in hospitalized patients: A cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:790–6. - PubMed
-
- Sastre J, Manso L, Sanchez-Garcia S, Fernandez-Nieto M. Medical and economic impact of misdiagnosis of drug hypersensitivity in hospitalized patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:566–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

