Patient selection and perioperative outcomes of bypass and endovascular intervention as first revascularization strategy for infrainguinal arterial disease
- PMID: 28844467
- PMCID: PMC5741492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.05.132
Patient selection and perioperative outcomes of bypass and endovascular intervention as first revascularization strategy for infrainguinal arterial disease
Abstract
Objective: The optimal initial revascularization strategy remains uncertain for patients with peripheral arterial disease. The purpose of this study was to evaluate current nationwide selection and perioperative outcomes of patients undergoing bypass or endovascular intervention for infrainguinal disease in those with no prior ipsilateral revascularization.
Methods: Patients undergoing nonemergent first-time infrainguinal revascularization were identified in the Targeted Vascular module of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) for 2011 to 2014 and stratified by symptom status (chronic limb-threatening ischemia [CLTI] or claudication). Patients treated with endovascular intervention were compared with those who underwent bypass. Multivariable logistic regression was used to evaluate current selection of patients and to establish independent associations between first-time procedures and postoperative outcomes.
Results: Of 5998 first-time infrainguinal revascularizations performed, 3193 were bypass procedures (63% for CLTI) and 2805 were endovascular interventions (64% for CLTI). Current patient characteristics associated with an endovascular-first approach as opposed to bypass-first in CLTI patients were age ≥80 years, tissue loss, nonsmoking, functional dependence, diabetes, dialysis, and tibial lesions, whereas age ≥80 years, nonwhite race, nonsmoking, diabetes, and tibial lesions were associated with an endovascular approach for claudication. In comparing first-time endovascular intervention with bypass, there was no difference in 30-day mortality in CLTI patients (univariate: 2.1% vs 2.2%; adjusted: odds ratio [OR], 0.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.4-1.1) or claudication patients (0.3% vs 0.6%). Among CLTI patients, endovascular-first intervention was associated with lower rates of major adverse cardiovascular event (3.6% vs 4.7%; OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.4-0.9), surgical site infection (0.9% vs 7.7%; OR, 0.1; 95% CI, 0.1-0.2), bleeding (8.5% vs 17%; OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.3-0.5), unplanned reoperation (13% vs 17%; OR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.5-0.8), and unplanned readmission (17% vs 18%; OR, 0.8; 95% CI, 0.7-0.9). Patients with claudication undergoing endovascular-first intervention also had lower rates of major adverse cardiovascular event (0.8% vs 1.6%; OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.2-0.95), surgical site infection (0.7% vs 6.6%; OR, 0.1; 95% CI, 0.04-0.2), bleeding (2.3% vs 6.0%; OR, 0.3; 95% CI, 0.2-0.5), unplanned reoperation (4.3% vs 6.6%; OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.4-0.9), and unplanned readmission (5.9% vs 9.0%; OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.4-0.8). Conversely, endovascular-first intervention was associated with a higher rate of secondary revascularizations within 30 days for CLTI (4.3% vs 3.1%; OR, 1.6; 95% CI, 1.04-2.3) but not for claudication (2.6% vs 1.9%; OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 0.9-3.4).
Conclusions: An endovascular-first approach as a revascularization strategy for infrainguinal disease was associated with substantially lower early morbidity but not mortality, at the cost of higher rates of postoperative secondary revascularizations. As a national representation of first-time revascularizations, this study highlights the early endovascular perioperative benefit, although more robust long-term data are needed to adopt either one strategy or the other in select patients with peripheral arterial disease.
Copyright © 2017 Society for Vascular Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


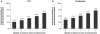
References
-
- Agarwal S, Sud K, Shishehbor MH. Nationwide Trends of Hospital Admission and Outcomes Among Critical Limb Ischemia Patients: From 2003-2011. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(16):1901–1913. - PubMed
-
- Rowe VL, Lee W, Weaver FA, Etzioni D. Patterns of treatment for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: 1996-2005. J Vasc Surg. 2009;49(4):910–917. - PubMed
-
- Goodney PP, Beck AW, Nagle J, Welch HG, Zwolak RM. National trends in lower extremity bypass surgery, endovascular interventions, and major amputations. J Vasc Surg. 2009;50(1):54–60. - PubMed
-
- Adam DJ, Beard JD, Cleveland T, Bell J, Bradbury AW, Forbes JF, et al. Bypass versus angioplasty in severe ischaemia of the leg (BASIL): multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366(9501):1925–1934. - PubMed
-
- van der Zaag ES, Legemate DA, Prins MH, Reekers JA, Jacobs MJ. Angioplasty or bypass for superficial femoral artery disease? A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004;28(2):132–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

