The Lymphotoxin β Receptor Is Essential for Upregulation of IFN-Induced Guanylate-Binding Proteins and Survival after Toxoplasma gondii Infection
- PMID: 28845089
- PMCID: PMC5563413
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7375818
The Lymphotoxin β Receptor Is Essential for Upregulation of IFN-Induced Guanylate-Binding Proteins and Survival after Toxoplasma gondii Infection
Abstract
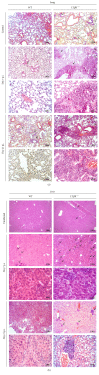
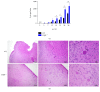
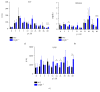
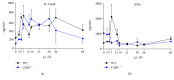
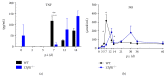
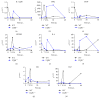
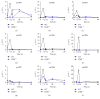
Lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR) signaling plays an important role in efficient initiation of host responses to a variety of pathogens, encompassing viruses, bacteria, and protozoans via induction of the type I interferon response. The present study reveals that after Toxoplasma gondii infection, LTβR-/- mice show a substantially reduced survival rate when compared to wild-type mice. LTβR-/- mice exhibit an increased parasite load and a more pronounced organ pathology. Also, a delayed increase of serum IL-12p40 and a failure of the protective IFNγ response in LTβR-/- mice were observed. Serum NO levels in LTβR-/- animals rose later and were markedly decreased compared to wild-type animals. At the transcriptional level, LTβR-/- animals exhibited a deregulated expression profile of several cytokines known to play a role in activation of innate immunity in T. gondii infection. Importantly, expression of the IFNγ-regulated murine guanylate-binding protein (mGBP) genes was virtually absent in the lungs of LTβR-/- mice. This demonstrates clearly that the LTβR is essential for the induction of a type II IFN-mediated immune response against T. gondii. The pronounced inability to effectively upregulate host defense effector molecules such as GBPs explains the high mortality rates of LTβR-/- animals after T. gondii infection.
Figures


References
-
- Ehlers S., Hölscher C., Scheu S., et al. The lymphotoxin beta receptor is critically involved in controlling infections with the intracellular pathogens mycobacterium tuberculosis and Listeria monocytogenes. Journal of Immunology. 2003;170(10):5210–5218. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.10.5210. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

