Eyelid Molluscum Contagiosum Lesions in Two Patients with Unilateral Chronic Conjunctivitis
- PMID: 28845328
- PMCID: PMC5563552
- DOI: 10.4274/tjo.52138
Eyelid Molluscum Contagiosum Lesions in Two Patients with Unilateral Chronic Conjunctivitis
Abstract
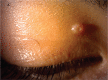
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a viral infection of the skin and mucosal tissues characterized by skin-colored or transparent round nodules with a dimple or pit in the center. The infection is caused by a DNA poxvirus called the MC virus. Although MC generally occurs in children, it has also been reported in immunocompromised and atopic patients. The virus is transmitted by skin contact or sexual intercourse. The lesions disappear spontaneously within several months in most cases. However, excision, cryotherapy, cauterization, topical chemical and antiviral agents, and/or oral cimetidine are used in refractory cases or to accelerate the healing process. Herein, we discussed the clinical findings and our treatment of two patients with unilateral chronic conjunctivitis associated with eyelid MC lesions in light of the literature.
Keywords: Molluscum contagiosum; chronic conjunctivitis; eyelid lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures







References
-
- Moyes AL, Verachtert AJ. Eyelid Infections. In: Krachmer JH, Mannis MJ, Holland EJ, editors. Cornea. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 415–424.
-
- Laxmisha C, Thappa DM, Jaisankar TJ. Clinical profile of molluscum contagiosum in children versus adults. Dermatology Online J. 2003;9:1. - PubMed
-
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, Lucky AW, Paller AS, Eichenfield LF. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay DN, Basak SK, Ghose S. HIV-positive patient presented with giant molluscum contagiosum of the eyelid. J Indian Med Assoc. 1997;95:202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
