ZSCAN10 expression corrects the genomic instability of iPSCs from aged donors
- PMID: 28846095
- PMCID: PMC5843481
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3598
ZSCAN10 expression corrects the genomic instability of iPSCs from aged donors
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: ZSCAN10 expression corrects the genomic instability of iPSCs from aged donors.Nat Cell Biol. 2019 Apr;21(4):531-532. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0269-y. Nat Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30643186
Abstract
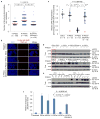
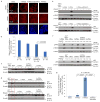
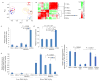
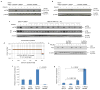
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are used to produce transplantable tissues, may particularly benefit older patients, who are more likely to suffer from degenerative diseases. However, iPSCs generated from aged donors (A-iPSCs) exhibit higher genomic instability, defects in apoptosis and a blunted DNA damage response compared with iPSCs generated from younger donors. We demonstrated that A-iPSCs exhibit excessive glutathione-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activity, which blocks the DNA damage response and apoptosis and permits survival of cells with genomic instability. We found that the pluripotency factor ZSCAN10 is poorly expressed in A-iPSCs and addition of ZSCAN10 to the four Yamanaka factors (OCT4, SOX2, KLF4 and c-MYC) during A-iPSC reprogramming normalizes ROS-glutathione homeostasis and the DNA damage response, and recovers genomic stability. Correcting the genomic instability of A-iPSCs will ultimately enhance our ability to produce histocompatible functional tissues from older patients' own cells that are safe for transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
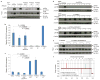
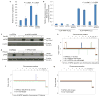
References
-
- Kang E, et al. Age-related accumulation of somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in adult-derived human iPSCs. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18:625–636. - PubMed
-
- Garber K. RIKEN suspends first clinical trial involving induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:890–891. - PubMed
-
- Coghlan A. Unexpected mutations put stem cell trial on hold. New Sci. 2015;227:9.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

