Rare, high-affinity mouse anti-PD-1 antibodies that function in checkpoint blockade, discovered using microfluidics and molecular genomics
- PMID: 28846506
- PMCID: PMC5680806
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2017.1371386
Rare, high-affinity mouse anti-PD-1 antibodies that function in checkpoint blockade, discovered using microfluidics and molecular genomics
Abstract
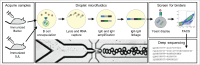
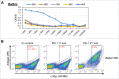
Conventionally, mouse hybridomas or well-plate screening are used to identify therapeutic monoclonal antibody candidates. In this study, we present an alternative to hybridoma-based discovery that combines microfluidics, yeast single-chain variable fragment (scFv) display, and deep sequencing to rapidly interrogate and screen mouse antibody repertoires. We used our approach on six wild-type mice to identify 269 molecules that bind to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), which were present at an average of 1 in 2,000 in the pre-sort scFv libraries. Two rounds of fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) produced populations of PD-1-binding scFv with a mean enrichment of 800-fold, whereas most scFv present in the pre-sort mouse repertoires were de-enriched. Therefore, our work suggests that most of the antibodies present in the repertoires of immunized mice are not strong binders to PD-1. We observed clusters of related antibody sequences in each mouse following FACS, suggesting evolution of clonal lineages. In the pre-sort repertoires, these putative clonal lineages varied in both the complementary-determining region (CDR)3K and CDR3H, while the FACS-selected PD-1-binding subsets varied primarily in the CDR3H. PD-1 binders were generally not highly diverged from germline, showing 98% identity on average with germline V-genes. Some CDR3 sequences were discovered in more than one animal, even across different mouse strains, suggesting convergent evolution. We synthesized 17 of the anti-PD-1 binders as full-length monoclonal antibodies. All 17 full-length antibodies bound recombinant PD-1 with KD < 500 nM (average = 62 nM). Fifteen of the 17 full-length antibodies specifically bound surface-expressed PD-1 in a FACS assay, and nine of the antibodies functioned as checkpoint inhibitors in a cellular assay. We conclude that our method is a viable alternative to hybridomas, with key advantages in comprehensiveness and turnaround time.
Keywords: PD-1; checkpoint inhibitors; deep sequencing; microfluidics; mouse repertoire; yeast display.
Figures


References
-
- Reddy ST, Ge X, Miklos AE, Hughes RA, Kang SH, Hoi KH, Chrysostomou C, Hunicke-Smith SP, Iverson BL, Tucker PW, et al.. Monoclonal antibodies isolated without screening by analyzing the variable-gene repertoire of plasma cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(9):965-9. doi:10.1038/nbt.1673. PMID:20802495 - DOI - PubMed
-
- DeKosky BJ, Ippolito GC, Deschner RP, Lavinder JJ, Wine Y, Rawlings BM, Varadarajan N, Giesecke C, Dörner T, Andrews SF, et al.. High-throughput sequencing of the paired human immunoglobulin heavy and light chain repertoire. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:166-9. doi:10.1038/nbt.2492. PMID:23334449 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
