Swimming Training Reduces Neuroma Pain by Regulating Neurotrophins
- PMID: 28846565
- PMCID: PMC5757647
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001411
Swimming Training Reduces Neuroma Pain by Regulating Neurotrophins
Abstract
Introduction: Neuroma formation after peripheral nerve transection leads to severe neuropathic pain in amputees. Previous studies suggested that physical exercise could bring beneficial effect on alleviating neuropathic pain. However, the effect of exercise on neuroma pain still remained unclear. In addition, long-term exercise can affect the expression of neurotrophins (NT), such as nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which play key roles in nociceptor sensitization and nerve sprouting after nerve injury. Here, we investigated whether long-term swimming exercise could relieve neuroma pain by modulating NT expression.
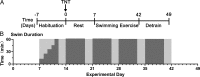
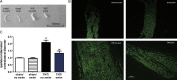
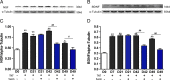
Methods: We used a tibial neuroma transposition (TNT) rat model to mimic neuroma pain. After TNT surgery, rats performed swimming exercise for 5 wk. Neuroma pain and tactile sensitivities were detected using von Frey filaments. Immunofluorescence was applied to analyze neuroma formation. NGF and BDNF expressions in peripheral neuroma, dorsal root ganglion, and the spinal cord were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting.
Results: TNT led to neuroma formation, induced neuroma pain, and mechanical allodynia in hind paw. Five-week swimming exercise inhibited neuroma formation and relieved mechanical allodynia in the hind paw and neuroma pain in the lateral ankle. The analgesic effect lasted for at least 1 wk, even when the exercise ceased. TNT elevated the expressions of BDNF and NGF in peripheral neuroma, dorsal root ganglion, and the spinal cord to different extents. Swimming also decreased the elevation of NT expression.
Conclusions: Swimming exercise not only inhibits neuroma formation induced by nerve transection but also relieves pain behavior. These effects might be associated with the modulation of NT.
Figures


References
-
- Fang J, Lian YH, Xie KJ, Cai SN. Pharmacological interventions for phantom limb pain. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(3):542–9. - PubMed
-
- Hill A. Phantom limb pain: a review of the literature on attributes and potential mechanisms. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1999;17(2):125–42. - PubMed
-
- Rajput K, Reddy S, Shankar H. Painful neuromas. Clin J Pain. 2012;28(7):639–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

