Current Status and Future Prospects of Marine Natural Products (MNPs) as Antimicrobials
- PMID: 28846659
- PMCID: PMC5618411
- DOI: 10.3390/md15090272
Current Status and Future Prospects of Marine Natural Products (MNPs) as Antimicrobials
Abstract
The marine environment is a rich source of chemically diverse, biologically active natural products, and serves as an invaluable resource in the ongoing search for novel antimicrobial compounds. Recent advances in extraction and isolation techniques, and in state-of-the-art technologies involved in organic synthesis and chemical structure elucidation, have accelerated the numbers of antimicrobial molecules originating from the ocean moving into clinical trials. The chemical diversity associated with these marine-derived molecules is immense, varying from simple linear peptides and fatty acids to complex alkaloids, terpenes and polyketides, etc. Such an array of structurally distinct molecules performs functionally diverse biological activities against many pathogenic bacteria and fungi, making marine-derived natural products valuable commodities, particularly in the current age of antimicrobial resistance. In this review, we have highlighted several marine-derived natural products (and their synthetic derivatives), which have gained recognition as effective antimicrobial agents over the past five years (2012-2017). These natural products have been categorized based on their chemical structures and the structure-activity mediated relationships of some of these bioactive molecules have been discussed. Finally, we have provided an insight into how genome mining efforts are likely to expedite the discovery of novel antimicrobial compounds.
Keywords: antibacterial; antifungal; antimicrobial; genome mining; marine natural products (MNPs); secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
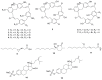
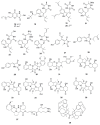

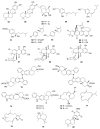

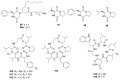
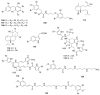


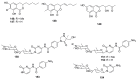
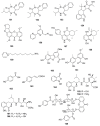
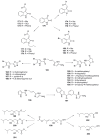
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

