Comparison of cognitive and brain grey matter volume profiles between multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder
- PMID: 28846745
- PMCID: PMC5573289
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184012
Comparison of cognitive and brain grey matter volume profiles between multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder
Abstract
Objective: Brain regions responsible for cognitive dysfunction in MS and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) are not known. Our aim of this study was to investigate whether cognitive function and brain volume differed between MS and NMOSD in Japanese patients.
Methods: Brain MRI and neuropsychological tests including the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-III (WAIS-III), Wechsler Memory Scale-Revised (WMS-R), Trail Making Test (TMT) and Clinical Assessment for Attention (CAT) were performed. Parametric grey matter (GM) and white matter (WM) volumes determined from lesion-filled T1-weighted images using whole-brain voxel-based morphometry (VBM) were compared by two-tailed t test.
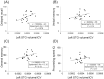
Results: Twenty relapsing-remitting MS and sixteen NMOSD patients were included. MS patients were younger than NMOSD patients. Processing speed intelligence quotient (IQ), general memory, verbal memory and delayed recall were significantly worse in MS patients than in NMOSD patients. Furthermore, left superior temporal gyrus (STG) GM volume was smaller in MS patients than in NMOSD patients (P < 0.05, family-wise error [FWE] corrected, Zmax = 4.97, 62 voxel). The left STG GM volume tended to be positively correlated with delayed recall in MS patients.
Conclusions: Despite being younger, MS patients demonstrated worse performance in certain cognitive variables than NMOSD patients, which might be associated with left STG GM volume loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Alexander Rae-Grant M, Fox R, Bethoux F. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders: Diagnosis, Medical Management, and Rehabilitation: Demos Medical Publishing; 2013.
-
- Blanc F, Zéphir H, Lebrun C, Labauge P, Castelnovo G, Fleury M, et al. Cognitive functions in neuromyelitis optica. Archives of Neurology. 2008;65(1):84–8. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2007.16 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moore P, Methley A, Pollard C, Mutch K, Hamid S, Elsone L, et al. Cognitive and psychiatric comorbidities in neuromyelitis optica. J Neurol Sci. 2016;360:4–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.11.031 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saji E, Arakawa M, Yanagawa K, Toyoshima Y, Yokoseki A, Okamoto K, et al. Cognitive impairment and cortical degeneration in neuromyelitis optica. Annals of neurology. 2013;73(1):65–76. doi: 10.1002/ana.23721 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Prinster A, Quarantelli M, Orefice G, Lanzillo R, Brunetti A, Mollica C, et al. Grey matter loss in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a voxel-based morphometry study. Neuroimage. 2006;29(3):859–67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.08.034 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

