XLF/Cernunnos: An important but puzzling participant in the nonhomologous end joining DNA repair pathway
- PMID: 28846869
- PMCID: PMC6685063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.08.003
XLF/Cernunnos: An important but puzzling participant in the nonhomologous end joining DNA repair pathway
Abstract
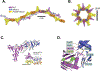
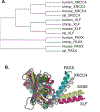
DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) are one of the most deleterious DNA lesions that promote cell death, genomic instability and carcinogenesis. The two major cellular mechanisms that repair DSBs are Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) and Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR). NHEJ is the predominant pathway, in which XLF (also called Cernunnos) is a key player. Patients with XLF mutation exhibit microcephaly, lymphopenia, and growth retardation, and are immunodeficient and radiosensitive. During NHEJ, XLF interacts with XRCC4-Ligase IV, stimulates its ligase activity, and forms DNA-binding filaments of alternating XLF and XRCC4 dimers that may serve to align broken DNA and promote ligation of noncomplementary ends. Despite its central role in NHEJ, the effects of XLF deficiency are surprisingly variable in different biological contexts, and different individual cell lines. This review summarizes the role of XLF in NHEJ, and the unexpected complexity of its interplay with other repair factors in supporting radiosurvival and V(D)J recombination.
Keywords: Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ); V(D)J recombination; XLF/Cernunnos; XRCC4.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
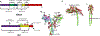


References
-
- Povirk LF DNA damage and mutagenesis by radiomimetic DNA-cleaving agents: Bleomycin, neocarzinostatin and other enediynes, Mutat. Res 355 (1996) 71–89. - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson F Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation, Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol 32 (1985) 115–154. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J, Ravanat JL, TavernaPorro M, Menoni H, Angelov D Oxidatively generated complex DNA damage: Tandem and clustered lesions, Cancer Lett 327 (2012) 5–15. - PubMed
-
- Valerie K, Povirk LF Regulation and mechanisms of mammalian double-strand break repair, Oncogene 22 (2003) 5792–5812. - PubMed
-
- Walker JR, Corpina RA, Goldberg J Structure of the Ku heterodimer bound to DNA and its implications for double-strand break repair, Nature 412 (2001) 607–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

