Lhx6-positive GABA-releasing neurons of the zona incerta promote sleep
- PMID: 28847002
- PMCID: PMC5958617
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23663
Lhx6-positive GABA-releasing neurons of the zona incerta promote sleep
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Lhx6-positive GABA-releasing neurons of the zona incerta promote sleep.Nature. 2017 Oct 26;550(7677):548. doi: 10.1038/nature24274. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28953871 Free PMC article.
Abstract
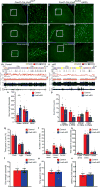
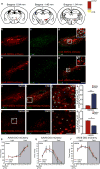
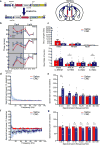
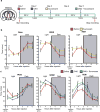
Multiple populations of wake-promoting neurons have been characterized in mammals, but few sleep-promoting neurons have been identified. Wake-promoting cell types include hypocretin and GABA (γ-aminobutyric-acid)-releasing neurons of the lateral hypothalamus, which promote the transition to wakefulness from non-rapid eye movement (NREM) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Here we show that a subset of GABAergic neurons in the mouse ventral zona incerta, which express the LIM homeodomain factor Lhx6 and are activated by sleep pressure, both directly inhibit wake-active hypocretin and GABAergic cells in the lateral hypothalamus and receive inputs from multiple sleep-wake-regulating neurons. Conditional deletion of Lhx6 from the developing diencephalon leads to decreases in both NREM and REM sleep. Furthermore, selective activation and inhibition of Lhx6-positive neurons in the ventral zona incerta bidirectionally regulate sleep time in adult mice, in part through hypocretin-dependent mechanisms. These studies identify a GABAergic subpopulation of neurons in the ventral zona incerta that promote sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
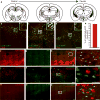
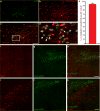
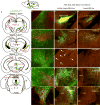
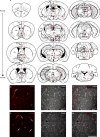

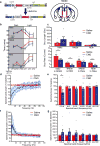
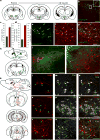
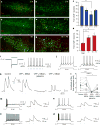
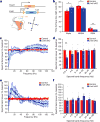
References
-
- Weber F, Dan Y. Circuit-based interrogation of sleep control. Nature. 2016;538:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, et al. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Mitrofanis J. Some certainty for the “zone of uncertainty”? Exploring the function of the zona incerta. Neuroscience. 2005;130:1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

