PI3K: A Crucial Piece in the RAS Signaling Puzzle
- PMID: 28847905
- PMCID: PMC5983164
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a031450
PI3K: A Crucial Piece in the RAS Signaling Puzzle
Abstract
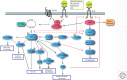
RAS proteins are key signaling switches essential for control of proliferation, differentiation, and survival of eukaryotic cells. RAS proteins are mutated in 30% of human cancers. In addition, mutations in upstream or downstream signaling components also contribute to oncogenic activation of the pathway. RAS proteins exert their functions through activation of several signaling pathways and dissecting the contributions of these effectors in normal cells and in cancer is an ongoing challenge. In this review, we summarize our current knowledge about how RAS regulates type I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), one of the main RAS effectors. RAS signaling through PI3K is necessary for normal lymphatic vasculature development and for RAS-induced transformation in vitro and in vivo, especially in lung cancer, where it is essential for tumor initiation and necessary for tumor maintenance.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aksamitiene E, Kiyatkin A, Kholodenko BN. 2012. Cross-talk between mitogenic Ras/MAPK and survival PI3K/Akt pathways: A fine balance. Biochem Soc Trans 40: 139–146. - PubMed
-
- Asati V, Mahapatra DK, Bharti SK. 2017. K-Ras and its inhibitors towards personalized cancer treatment: Pharmacological and structural perspectives. Eur J Med Chem 125: 299–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
