Visual field examination method using virtual reality glasses compared with the Humphrey perimeter
- PMID: 28848325
- PMCID: PMC5557117
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S131160
Visual field examination method using virtual reality glasses compared with the Humphrey perimeter
Abstract
Purpose: To present a visual field examination method using virtual reality glasses and evaluate the reliability of the method by comparing the results with those of the Humphrey perimeter.
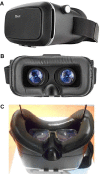
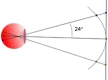
Materials and methods: Virtual reality glasses, a smartphone with a 6 inch display, and software that implements a fast-threshold 3 dB step staircase algorithm for the central 24° of visual field (52 points) were used to test 20 eyes of 10 patients, who were tested in a random and consecutive order as they appeared in our glaucoma department. The results were compared with those obtained from the same patients using the Humphrey perimeter.
Results: High correlation coefficient (r=0.808, P<0.0001) was found between the virtual reality visual field test and the Humphrey perimeter visual field.
Conclusion: Visual field examination results using virtual reality glasses have a high correlation with the Humphrey perimeter allowing the method to be suitable for probable clinical use.
Keywords: perimetry; smartphone; virtual reality glasses; visual fields; visual fields software.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


















References
-
- John R, Kasha, inventors. Kasha, John R, assignee Visual field perimetry using virtual reality glasses. US5737060A. United States patent. 1998 Apr 7;
-
- Chan ADC, Eizenman M, Flanagan J, Trope G. Vision Science and Its Applications. Optical Society of America; Washington, DC: USA: Feb 19, 1999. Head-mounted perimetry. (OSA Technical Digest Series). Paper MB1.
-
- Colombo E, Derrington A. Visual calibration of CRT monitors. Displays. 2001;22(3):87–95.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

