Water-Deficit Tolerance in Sweet Potato [ Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] by Foliar Application of Paclobutrazol: Role of Soluble Sugar and Free Proline
- PMID: 28848596
- PMCID: PMC5550687
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01400
Water-Deficit Tolerance in Sweet Potato [ Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] by Foliar Application of Paclobutrazol: Role of Soluble Sugar and Free Proline
Abstract
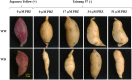
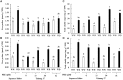
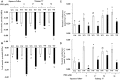
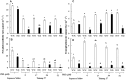
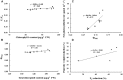
The objective of this study was to elevate water deficit tolerance by improving soluble sugar and free proline accumulation, photosynthetic pigment stabilization, photosynthetic abilities, growth performance and storage root yield in sweet potato cv. 'Tainung 57' using a foliar application of paclobutrazol (PBZ). The experiment followed a Completely Randomized Block Design with four concentrations of PBZ: 0 (control), 17, 34, and 51 μM before exposure to 47.5% (well irrigation), 32.3% (mild water deficit) or 17.5% (severe water deficit) soil water content. A sweet potato cultivar, 'Japanese Yellow', with water deficit tolerance attributes was the positive check in this study. Total soluble sugar content (sucrose, glucose, and fructose) increased by 3.96-folds in 'Tainung 57' plants treated with 34 μM PBZ grown under 32.3% soil water content (SWC) compared to the untreated plants, adjusting osmotic potential in the leaves and controlling stomatal closure (represented by stomatal conductance and transpiration rate). In addition, under the same treatment, free proline content (2.15 μmol g-1 FW) increased by 3.84-folds when exposed to 17.5% SWC. PBZ had an improved effect on leaf size, vine length, photosynthetic pigment stability, chlorophyll fluorescence, and net photosynthetic rate; hence, delaying wilting symptoms and maintaining storage root yield (26.93 g plant-1) at the harvesting stage. A positive relationship between photon yield of PSII (ΦPSII) and net photosynthetic rate was demonstrated (r2 = 0.73). The study concludes that soluble sugar and free proline enrichment in PBZ-pretreated plants may play a critical role as major osmoprotectant to control leaf osmotic potential and stomatal closure when plants were subjected to low soil water content, therefore, maintaining the physiological and morphological characters as well as storage root yield.
Keywords: paclobutrazol; pigment; proline; sweet potato; total soluble sugar; water deficit.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad I., Whipker B. E., Dole J. M., McCall I. (2014). Paclobutrazol and ancymidol lower water use of potted ornamental plants and plugs. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 79, 318–326.
-
- Bañon S., Miralles J., Navarro A., Sánchez-Blanco M. J. (2009). Influence of paclobutrazol and substrate on daily evapotranspiration of potted geranium. Sci. Hortic. 122, 572–578.
-
- Bates L. S., Waldren R. P., Teare I. D. (1973). Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39, 205–207. 10.1016/j.dental.2010.07.006 - DOI
-
- Bayat S., Sepehri A. (2012). Paclobutrazol and salicylic acid application ameliorates the negative effect of water stress on growth and yield of maize plants. J. Res. Agric. Sci. 8, 127–139.
-
- Berova M., Zlatev Z. (2003). Physiological response of paclobutrazol-treated triticale plants to water stress. Biol. Plant. 46, 133–136.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

