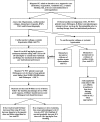
Pulmonary Embolism in Children
- PMID: 28848725
- PMCID: PMC5554122
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2017.00170
Pulmonary Embolism in Children
Abstract
Pulmonary embolism (PE) in the pediatric population is relatively rare when compared to adults; however, the incidence is increasing and accurate and timely diagnosis is critical. A high clinical index of suspicion is warranted as PE often goes unrecognized among children leading to misdiagnosis and potentially increased morbidity and mortality. Evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of children with PE are lacking and current practices are extrapolated from adult data. Treatment options include thrombolysis and anticoagulation with heparins and oral vitamin K antagonists, with newer direct oral anticoagulants currently in clinical trials. Long-term sequelae of PE, although studied in adults, are vastly unknown among children and adolescents. Additional research is needed in order to provide pediatric focused care for patients with acute PE.
Keywords: children; deep venous thrombosis; pediatrics; pulmonary artery thrombosis; pulmonary embolism.
Figures
References
-
- von Löschner JWF. Phlebitis venae cruralis sinistrae, peri-et myocarditis, embolia et oedema pulmonum. Jahrb f Kenderh (1861) 4:6.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources