Robotic hepatectomy: the Korean experience and perspective
- PMID: 28848745
- PMCID: PMC5554764
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2017.01.14
Robotic hepatectomy: the Korean experience and perspective
Abstract
Since the robotic surgical system was first introduced in 2005, the number of robotic surgery has been gradually increasing in Korea. The proportion of general robotic surgery is relatively higher compared to the western countries, but robotic liver resection is one of the most complex procedures among robotic general surgery. In this article, we introduce the development of robotic liver resection in Korea and describe our standardized techniques. The current data on robotic liver resection in our institute and other centers in Korea are also presented.
Keywords: Robotic liver resection; anatomic liver resection; minimally invasive liver resection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
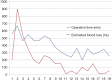
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
