Pharmacologic Manipulation of Wnt Signaling and Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 28849572
- PMCID: PMC7473415
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7027-8_18
Pharmacologic Manipulation of Wnt Signaling and Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
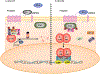
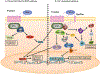
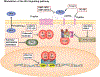
Wnt (Wingless-related integration site)-signaling orchestrates self-renewal programs in normal somatic stem cells as well as in cancer stem cells. Aberrant Wnt signaling is associated with a wide variety of malignancies and diseases. Although our understanding has increased tremendously over the past decade, therapeutic targeting of the dysregulated Wnt pathway remains a challenge. Here we review recent preclinical and clinical therapeutic approaches to target the Wnt pathway.
Keywords: Cancer stem cells; Clinical trial; Drug resistance; Self-renewal; Somatic stem cells; Wnt signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Reya T et al. (2001) Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 414(6859):105–111 - PubMed
-
- Liu J et al. (2010) Notch signaling in the regulation of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol 92:367–409 - PubMed
-
- Miki T, Yasuda S-y, Kahn M (2011) Wnt/β-catenin signaling in embryonic stem cell self-renewal and somatic cell reprogramming. Stem Cell Rev Rep 7(4):836–846 - PubMed
-
- Takahashi-Yanaga F, Kahn M (2010) Targeting Wnt signaling: can we safely eradicate cancer stem cells? Clin Cancer Res 16 (12):3153–3162 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

