Antialbuminuric effect of eplerenone in comparison to thiazide diuretics in patients with hypertension
- PMID: 28849629
- PMCID: PMC8031246
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13054
Antialbuminuric effect of eplerenone in comparison to thiazide diuretics in patients with hypertension
Abstract
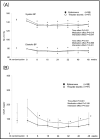
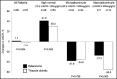
This study investigated the effects and safety of eplerenone or thiazide diuretics in patients with hypertension and albuminuria (pretreatment urinary albumin/creatinine ratio ≥10 mg/gCr) treated with an angiotensin II receptor blocker. The primary end point was the mean percent change in the urinary albumin/creatinine ratio from baseline to 48 weeks. An efficacy analysis was performed in 195 patients (98 in the eplerenone group and 97 in the thiazide group). Systolic and diastolic blood pressures at 48 weeks were similar in the two groups. The mean percent change in the urinary albumin/creatinine ratio from baseline to 48 weeks was similar in the two groups (P=.804). In the safety analysis, the withdrawal rates for adverse events were similar in both groups. The antialbuminuric effects and safety of eplerenone therapy were similar to those of thiazide diuretics when combined with an angiotensin II receptor blocker in patients with hypertension and albuminuria.
Keywords: antihypertensive therapy; clinical trials; combination therapy; proteinuria; renal disease.
©2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Toshiki Sawai, Setsuya Okubo, Naoki Isaka, Takehiko Ichikawa, Katsutoshi Makino, Shinya Okamoto, Sukenari Koyabu, Naoki Fujimoto, Toru Ogura, Tomomi Yamada, and Satoshi Tamaru have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association councils on kidney in cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure research, clinical cardiology, and epidemiology and prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154‐2169. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura K, Okamura T, Hayakawa T, et al. Chronic kidney disease is a risk factor for cardiovascular death in a community‐based population in Japan: NIPPON DATA90. Circ J. 2006;70:954‐959. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296‐1305. - PubMed
-
- Irie F, Iso H, Sairenchi T, et al. The relationships of proteinuria, serum creatinine, glomerular filtration rate with cardiovascular disease mortality in Japanese general population. Kidney Int. 2006;69:1264‐1271. - PubMed
-
- Casas JP, Chua W, Loukogeorgakis S, et al. Effect of inhibitors of the renin‐angiotensin system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet. 2005;366:2026‐2033. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

