Acute Kidney Injury in Heart Failure Revisited-The Ameliorating Impact of "Decongestive Diuresis" on Renal Dysfunction in Type 1 Acute Cardiorenal Syndrome: Accelerated Rising Pro B Naturetic Peptide Is a Predictor of Good Renal Prognosis
- PMID: 28850085
- PMCID: PMC5615275
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm6090082
Acute Kidney Injury in Heart Failure Revisited-The Ameliorating Impact of "Decongestive Diuresis" on Renal Dysfunction in Type 1 Acute Cardiorenal Syndrome: Accelerated Rising Pro B Naturetic Peptide Is a Predictor of Good Renal Prognosis
Abstract
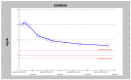
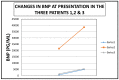
There is mounting evidence that forward heart failure as manifested by low cardiac output alone does not define the degree of renal dysfunction in cardiorenal syndrome. As a result, the term "congestive renal failure" was coined in 2012 by Ross to depict the role of renal venous hypertension in type 1 acute cardiorenal syndrome. If so, aggressive decongestive therapies, either through mechanical ultrafiltration with dialysis machines or pharmacologic ultrafiltration with potent diuretics, would lead to improved cardio and renal outcomes. Nevertheless, as recently as 2012, a review of this literature had concluded that a renal venous hypertension-directed approach using diuretics to manage cardio-renal syndrome was yet to be fully investigated. We, in this review, with three consecutive case series, describe our experience with pharmacologic decongestive diuresis in this paradigm of care and argue for studies of such therapeutic interventions in the management of cardiorenal syndrome. Finally, based on our observations in the Renal Unit, Mayo Clinic Health System, in Northwestern Wisconsin, we have hypothesized that patients with cardiorenal syndrome presenting with accelerated rising Pro B Naturetic Peptide levels appear to represent a group that would have good cardio- and renal-outcomes with such decongestive pharmacologic therapies.
Keywords: Pro B Naturetic Peptide; acute decompensated heart failure; cardiorenal syndrome; central venous pressure; congestive heart failure; congestive renal failure; continuous intravenous furosemide infusion; fluid balance; intravenous chlorothiazide; intravenous decongestive diuresis; renal venous hypertension; renal venous pressure; serum creatinine; ultrafiltration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Heywood J.T., Fonarow G.C., Costanzo M.R., Mathur V.S., Wigneswaran J.R., Wynne J. ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators. High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on outcome in 118,465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: A report from the ADHERE database. J. Card. Fail. 2007;13:422–430. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.03.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Damman K., van Deursen V.M., Navis G., Voors A.A., van Veldhuisen D.J., Hillege H.L. Increased central venous pressure is associated with impaired renal function and mortality in a broad spectrum of patients with cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009;53:582–588. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.08.080. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Damman K., Voors A.A., Hillege H.L., Navis G., Lechat P., van Veldhuisen D.J., Dargie H.J. CIBIS-2 Investigators and Committees. Congestion in chronic systolic heart failure is related to renal dysfunction and increased mortality. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010;12:974–982. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfq118. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

