Automatic Registration of TLS-TLS and TLS-MLS Point Clouds Using a Genetic Algorithm
- PMID: 28850100
- PMCID: PMC5621137
- DOI: 10.3390/s17091979
Automatic Registration of TLS-TLS and TLS-MLS Point Clouds Using a Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
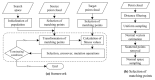
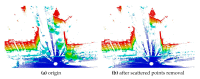
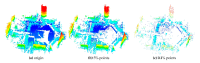
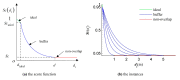
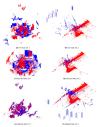
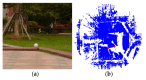
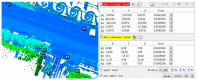
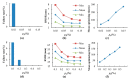
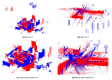
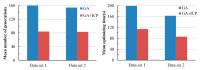
Registration of point clouds is a fundamental issue in Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) remote sensing because point clouds scanned from multiple scan stations or by different platforms need to be transformed to a uniform coordinate reference frame. This paper proposes an efficient registration method based on genetic algorithm (GA) for automatic alignment of two terrestrial LiDAR scanning (TLS) point clouds (TLS-TLS point clouds) and alignment between TLS and mobile LiDAR scanning (MLS) point clouds (TLS-MLS point clouds). The scanning station position acquired by the TLS built-in GPS and the quasi-horizontal orientation of the LiDAR sensor in data acquisition are used as constraints to narrow the search space in GA. A new fitness function to evaluate the solutions for GA, named as Normalized Sum of Matching Scores, is proposed for accurate registration. Our method is divided into five steps: selection of matching points, initialization of population, transformation of matching points, calculation of fitness values, and genetic operation. The method is verified using a TLS-TLS data set and a TLS-MLS data set. The experimental results indicate that the RMSE of registration of TLS-TLS point clouds is 3~5 mm, and that of TLS-MLS point clouds is 2~4 cm. The registration integrating the existing well-known ICP with GA is further proposed to accelerate the optimization and its optimizing time decreases by about 50%.
Keywords: genetic algorithm; mobile LiDAR scanning; point cloud; registration; terrestrial LiDAR scanning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yang B., Zang Y., Dong Z., Huang R. An automated method to register airborne and terrestrial laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015;109:62–76. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.08.006. - DOI
-
- Abbas M.A., Lichti D.D., Chong A.K., Setan H., Majid Z. An on-site approach for the self-calibration of terrestrial laser scanner. Measurement. 2014;52:111–123. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2014.03.009. - DOI
-
- Larsson S., Kjellander J.A.P. Motion control and data capturing for laser scanning with an industrial robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2006;54:453–460. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2006.02.002. - DOI
-
- Yastikli N. Documentation of cultural heritage using digital photogrammetry and laser scanning. J. Cult. Herit. 2007;8:423–427. doi: 10.1016/j.culher.2007.06.003. - DOI
-
- Ergincan F., Çabuk A., Avdan U., Tün M. Advanced technologies for archaeological documentation: Patara case. Sci. Res. Essays. 2010;5:2615–2629.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

