The effects of a lipid-based nutrient supplement and antiretroviral therapy in a randomized controlled trial on iron, copper, and zinc in milk from HIV-infected Malawian mothers and associations with maternal and infant biomarkers
- PMID: 28851037
- PMCID: PMC5832511
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12503
The effects of a lipid-based nutrient supplement and antiretroviral therapy in a randomized controlled trial on iron, copper, and zinc in milk from HIV-infected Malawian mothers and associations with maternal and infant biomarkers
Abstract
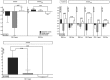
We evaluated effects of antiretroviral (ARV) therapy and lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNSs) on iron, copper, and zinc in milk of exclusively breastfeeding HIV-infected Malawian mothers and their correlations with maternal and infant biomarkers. Human milk and blood at 2, 6, and 24 weeks post-partum and blood during pregnancy (≤30 weeks gestation) were collected from 535 mothers/infant-pairs in the Breastfeeding, Antiretrovirals, and Nutrition study. The participants received ARV, LNS, ARV and LNS, or no intervention from 0 to 28 weeks post-partum. ARVs negatively affected copper and zinc milk concentrations, but only at 2 weeks, whereas LNS had no effect. Among all treatment groups, approximately 80-90% of copper and zinc and <50% of iron concentrations met the current adequate intake for infants at 2 weeks and only 1-19% at 24 weeks. Pregnancy haemoglobin was negatively correlated with milk iron at 2 and 6 weeks (r = -.18, p < .02 for both). The associations of the milk minerals with each other were the strongest correlations observed (r = .11-.47, p < .05 for all); none were found with infant biomarkers. At 2 weeks, moderately anaemic women produced milk higher in iron when ferritin was higher or TfR lower. At 6 weeks, higher maternal α-1-acid glycoprotein and C-reactive protein were associated with higher milk minerals in mildly anaemic women. Infant TfR was lower when milk mineral concentrations were higher at 6 weeks and when mothers were moderately anaemic during pregnancy. ARV affects copper and zinc milk concentrations in early lactation, and maternal haemoglobin during pregnancy and lactation could influence the association between milk minerals and maternal and infant iron status and biomarkers of inflammation.
Keywords: HIV; copper; haemoglobin status; human milk; iron; zinc.
© 2017 The Authors. Maternal and Child Nutrition Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
C. M. van der Horst received grant support from Abbott Laboratories and GlaxoSmithKline. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Adu‐Afarwuah, S. , Lartey, A. , Okronipa, H. , Ashorn, P. , Zeilani, M. , Peerson, J. M. , … Dewey, K. G. (2015). Lipid‐based nutrient supplement increases the birth size of infants of primiparous women in Ghana. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 101, 835–846. - PubMed
-
- Allen, L. H. , Hampel, D. , Shahab‐Ferdows, S. , York, E. R. , Adair, L. S. , Flax, V. L. , … Benltey, M. E. (2015). Antiretroviral therapy provided to HIV‐infected Malawian women in a randomized trial diminishes the positive effects of lipid‐based nutrient supplements on breast‐milk B vitamins. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 102, 1468–1476. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beshgetoor, D. , & Hambidge, M. (1998). Clinical conditions altering copper metabolism in humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 67(suppl.). 1017S‐1021S - PubMed
-
- Black, R. E. , Allen, L. H. , Bhutta, Z. A. , Caufield, L. E. , de Onis, M. , Ezzati, M. , … Rivera, J. (2008). Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. The Lancet, 371, 243–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

