Calmodulin inhibitor ameliorates cognitive dysfunction via inhibiting nitrosative stress and NLRP3 signaling in mice with bilateral carotid artery stenosis
- PMID: 28851042
- PMCID: PMC6492762
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12726
Calmodulin inhibitor ameliorates cognitive dysfunction via inhibiting nitrosative stress and NLRP3 signaling in mice with bilateral carotid artery stenosis
Abstract
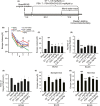
Aims: Vascular dementia (VaD) is a heterogeneous brain disorder for which there are no effective approved pharmacological treatments available. We aimed to evaluate the effect of calmodulin inhibitor, DY-9836, and its loaded nanodrug carrier system on cognitive impairment and gain a better understanding of the protective mechanisms in mice with bilateral carotid artery stenosis (BCAS).
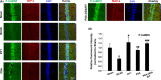
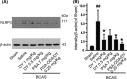
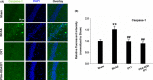
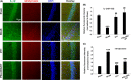
Results: DY-9836 (0.5 or 1 mg/kg) or DY-9836 (0.25 mg/kg)-encapsulated polysialic acid-octadecylamine (PSA-ODA) micelles (PSA-ODA/DY) were given to BCAS mice for 4 weeks. Administration of DY-9836 or PSA-ODA/DY reduced escape latency in space exploration and working memory test compared with vehicle group. Vehicle-treated mice showed reduced phospho-CaMKII (Thr286/287) levels in the hippocampus, whereas partially restored by DY-9836 (1 mg/kg) or PSA-ODA/DY (0.25 mg/kg) treatment. In accordance with the pharmacological profile of DY-9836 observed during behavioral studies, experimental molecular and biochemical markers induced by BCAS, such as protein tyrosine nitration, Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), caspase-1, and interleukin-1β, were reduced by DY-9836 and PSA-ODA/DY treatment.
Conclusions: These data disclose novel findings about the therapeutic potential of DY-9836, and its encapsulated nanodrug delivery system significantly enhanced the cognitive function via inhibitory effect on nitrosative stress and NLRP3 signaling in VaD mice.
Keywords: calmodulin inhibitor; cognitive impairment; inflammasome; nitrosative stress; vascular dementia.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous Polysialic Acid Based Micelles for Calmodulin Antagonist Delivery against Vascular Dementia.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Dec 28;8(51):35045-35058. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b13052. Epub 2016 Oct 26. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016. PMID: 27750011
-
Targeting NLRP3 signaling with a novel sulfonylurea compound for the treatment of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025 Jun 3;22(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12987-025-00665-6. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025. PMID: 40462117 Free PMC article.
-
ML365 ameliorates postoperative cognitive impairment in aged mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the hippocampus.Brain Res. 2024 Aug 15;1837:148957. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2024.148957. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 38663469
-
Hydrogen Attenuates Cognitive Impairment in Rat Models of Vascular Dementia by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Aug;13(20):e2400400. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202400400. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38769944
-
Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Instigates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Endothelial Dysfunction.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(1):152-162. doi: 10.1159/000484623. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29130962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the common mechanism of vascular dementia and inflammatory bowel disease: a bioinformatics-based study.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 25;15:1347415. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1347415. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38736878 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of low-dose Levamlodipine Besylate in the treatment of vascular dementia.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 3;9(1):18248. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47868-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31796756 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art: functional fluorescent probes for bioimaging and pharmacological research.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Jun;40(6):717-723. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0190-8. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30487651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in Cerebrovascular Diseases.Transl Stroke Res. 2021 Aug;12(4):513-529. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00901-9. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Transl Stroke Res. 2021. PMID: 33713030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium and Non-Penetrating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Proposal for the Implementation of an Early Therapeutic Treatment for Initial Head Insults.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 15;14(7):853. doi: 10.3390/biom14070853. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- O'Brien JT, Erkinjuntti T, Reisberg B, et al. Vascular cognitive impairment. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:89‐98. - PubMed
-
- Hachinski V, Iadecola C, Petersen RC, et al. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke‐Canadian Stroke Network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards. Stroke. 2006;37:2220‐2241. - PubMed
-
- Moorhouse P, Rockwood K. Vascular cognitive impairment: current concepts and clinical developments. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:246‐255. - PubMed
-
- Lobo A, Launer LJ, Fratiglioni L, et al. Prevalence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe: a collaborative study of population‐based cohorts. Neurologic diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology. 2000;54:S4‐S9. - PubMed
-
- Erkinjuntti T, Gauthier S. The concept of vascular cognitive impairment. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2009;24:79‐85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

