Dynamic imaging demonstrates that pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) suppress IL-6 transcription in bovine nucleus pulposus cells
- PMID: 28851112
- PMCID: PMC5873378
- DOI: 10.1002/jor.23713
Dynamic imaging demonstrates that pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) suppress IL-6 transcription in bovine nucleus pulposus cells
Abstract
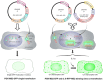
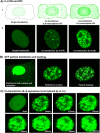
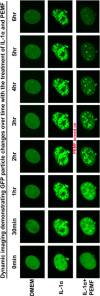
Inflammatory cytokines play a dominant role in the pathogenesis of disc degeneration. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) are noninvasive biophysical stimulus that has been used extensively in the orthopaedic field for many years. However, the specific cellular responses and mechanisms involved are still unclear. The objective of this study was to assess the time-dependent PEMF effects on pro-inflammatory factor IL-6 expression in disc nucleus pulposus cells using a novel green fluorescence protein (GFP) reporter system. An MS2-tagged GFP reporter system driven by IL-6 promoter was constructed to visualize PEMF treatment effect on IL-6 transcription in single living cells. IL-6-MS2 reporter-labeled cells were treated with IL-1α to mimic the in situ inflammatory environment of degenerative disc while simultaneously exposed to PEMF continuously for 4 h. Time-lapse imaging was recorded using a confocal microscope to track dynamic IL-6 transcription activity that was demonstrated by GFP. Finally, real-time RT-PCR was performed to confirm the imaging data. Live cell imaging demonstrated that pro-inflammatory factor IL-1α significantly promoted IL-6 transcription over time as compared with DMEM basal medium condition. Imaging and PCR data demonstrated that the inductive effect of IL-1α on IL-6 expression could be significantly inhibited by PEMF treatment in a time-dependent manner (early as 2 h of stimulus initiation). Our data suggest that PEMF may have a role in the clinical management of patients with chronic low back pain. Furthermore, this study shows that the MS2-tagged GFP reporter system is a useful tool for visualizing the dynamic events of mechanobiology in musculoskeletal research. © 2017 The Authors. Journal of Orthopaedic Research® Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Orthopaedic Research Society. J Orthop Res 35:778-787, 2018.
Keywords: IL-6 mRNA expression; MS2-GFP reporter; dynamic imaging; pulsed electromagnetic fields; spine/disc biology.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Orthopaedic Research® Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Orthopaedic Research Society.
Figures



References
-
- Katz JN. 2006. Lumbar disc disorders and low‐back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:21–24. - PubMed
-
- Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, et al. 2010. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease study. Ann Rheum Dis 73:968–974. - PubMed
-
- Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, et al. 2008. Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA 299:656–664. - PubMed
-
- Kao TH, Peng YJ, Tsou HK, et al. 2014. Nerve growth factor promotes expression of novel genes in intervertebral disc cells that regulate tissue degradation: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine 21:653–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

