Precisão e confiabilidade de um teste imuno-cromatográfico rápido NS1 para diagnóstico DENV-1 no ponto de atendimento e no laboratório
- PMID: 28851293
- PMCID: PMC5576130
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2679-z
Precisão e confiabilidade de um teste imuno-cromatográfico rápido NS1 para diagnóstico DENV-1 no ponto de atendimento e no laboratório
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Accuracy and reliability of an NS1 rapid immunochromatographic test for DENV-1 diagnosis at point of care and in the laboratory.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 1;17(1):710. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2804-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29092715 Free PMC article.
Abstract
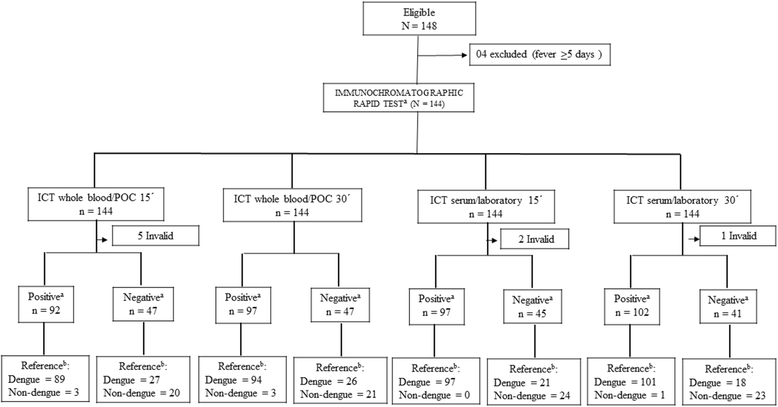
Background: Rapid immunochromatographic tests (ICT) for dengue non-structural protein 1 (NS1) have shown good performance for diagnosing acute-phase dengue in serum in laboratory settings, but rarely have been assessed in whole blood and at point of care (POC). This study compare the accuracy and inter- and intra-observer reliability of the NS1 Bioeasy™ ICT in whole blood at POC versus serum in the laboratory, during a DENV-1 epidemic.
Methods: Cross-sectional study involving 144 adults spontaneously demanding care in an emergency department within 4 days of onset of acute febrile illness. Accuracy of NS1 Bioeasy™ ICT was compared in whole blood and serum, both at 15 and 30 min, blinded to the reference RT-PCR or NS1 ELISA. Non-dengue patients were also tested for Zika virus with RT-PCR. Reliability of whole blood and serum readings by the same or different observers was measured by simple kappa (95% CI).
Results: At 15 min, sensitivity (Sn) of NS1 Bioeasy™ ICT in whole blood/POC was 76.7% (95% CI: 68.0-84.1) and specificity (Sp) was 87.0% (95% CI: 66.4-97.2). Sn in serum/laboratory was 82% (95% CI: 74.1-88.6) and Sp 100% (95% CI: 85.8-100). Positive likelihood ratio was 5.9 (95% CI: 2.0-17.0) for whole blood/POC and 19.8 (95% CI: 2.9-135.1) for serum/laboratory. Reliability of matched readings of whole blood/POC and serum/laboratory by the same observer (k = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74-0.93) or different observers (k = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.72-0.92) was almost perfect, with higher discordant levels in the absence of dengue. Results did not differ statistically at 5%.
Conclusions: NS1 Bioeasy™ ICT in DENV-1 epidemics is a potentially confirmatory test. Invalid results at 15 min should be reread at 30 min. To optimize impact of implementing ICT in the management of false-negatives it should be incorporated into an algorithm according to setting and available specimen.
Trial registration: UTN U1111-1145-9451 .
Keywords: Dengue; Diagnosis; NS1; Point-of-care systems; Reproducibility of results; Sensitivity and specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
O estudo foi aprovado pelo Conselho de Revisão Institucional do Instituto de Pesquisa Clínica Evandro Chagas (CAAE 0066.0.009.000-11). Todos os pacientes assinaram o formulário de consentimento livre e esclarecido.
Consentimento para publicação
Não aplicável.
Interesses competitivos
Os autores declaram que não têm interesses concorrentes.
Nota do editor
A Springer Nature permanece neutra em relação a reivindicações jurisdicionais em mapas publicados e afiliações institucionais.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of clinical criteria and an immunochromatographic strip test for dengue diagnosis in a DENV-4 epidemic.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Jan 29;16:37. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1368-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26822788 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic parameters and reliability of four rapid immunochromatographic tests for dengue 4.Braz J Infect Dis. 2020 Jan-Feb;24(1):58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2019.12.004. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Braz J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31954721 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of rapid diagnostic tests to detect dengue virus infections in Taiwan.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 29;15(9):e0239710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239710. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32991592 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of diagnostic and analytic performance of the SD Bioline Dengue Duo test for dengue virus (DENV) infections in an endemic area (Savannakhet province, Lao People's Democratic Republic).PLoS One. 2020 Mar 17;15(3):e0230337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230337. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32182271 Free PMC article.
-
False-Positive Nonstructural Protein 1 Antigen in a Patient with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Case Report with Literature Review.Am J Case Rep. 2021 Apr 9;22:e928865. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.928865. Am J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33835996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Molecular Aptamer Beacon Applied to Magnetic-Assisted RNA Extraction for Detection of Dengue and Zika Viruses Using Clinical Samples.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13866. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213866. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430340 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue fever as a reemerging disease in upper Egypt: Diagnosis, vector surveillance and genetic diversity using RT-LAMP assay.PLoS One. 2022 May 2;17(5):e0265760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265760. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35499983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Constenla D, Armien B, Arredondo J, Carabali M, Carrasquilla G, Castro R, et al. Custeio de casos de febre de dengue e surtos: recomendações de um grupo de trabalho de dengue de custo nas Américas. Valorar questões regionais de saúde. 2015;8C:80–91.
-
- Organização Mundial da Saúde. Dengue - diretrizes para diagnóstico, tratamento, prevenção e controle. Genebra: OMS; 2009. p. 11. Disponível em: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44188/1/9789241547871_eng.pdf. Accessed 9 Apr 2016
-
- Goodman C, Faulkner E, Gould C, Karnes E, Smith A, Aguiar C, et ai. O valor da inovação, adoção e difusão de diagnósticos nos cuidados de saúde. O grupo Lewin, inc. Adv Med. 2005; Disponível em: https://dx.advamed.org/sites/dx.advamed.org/files/resource/Lewin%20Value.... Acessado em 15 de dezembro de 2016
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials