Phospholipid Phosphatase 4 promotes proliferation and tumorigenesis, and activates Ca2+-permeable Cationic Channel in lung carcinoma cells
- PMID: 28851360
- PMCID: PMC5576330
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0717-5
Phospholipid Phosphatase 4 promotes proliferation and tumorigenesis, and activates Ca2+-permeable Cationic Channel in lung carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Phospholipid phosphatase 4 (PPAPDC1A or PLPP4) has been demonstrated to be involved in the malignant process of many cancers. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical significance and biological roles of PLPP4 in lung carcinoma.
Methods: PLPP4 expression was examined in 8 paired lung carcinoma tissues by real-time PCR and in 265 lung carcinoma tissues by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Statistical analysis was performed to evaluate the clinical correlation between PLPP4 expression and clinicopathological features and survival in lung carcinoma patients. In vitro and in vivo assays were performed to assess the biological roles of PLPP4 in lung carcinoma. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting, Western blotting and luciferase assays were used to identify the underlying pathway through which PLPP4 silencing mediates biological roles in lung carcinoma.
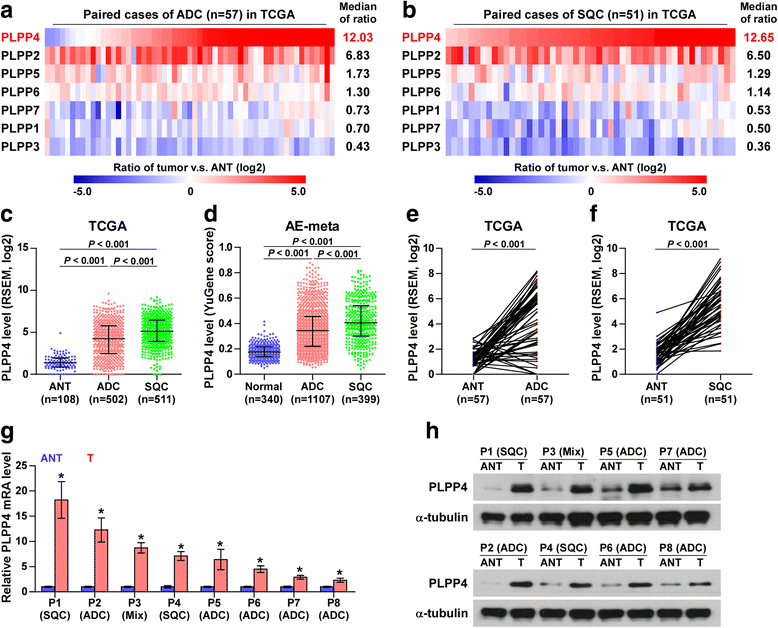
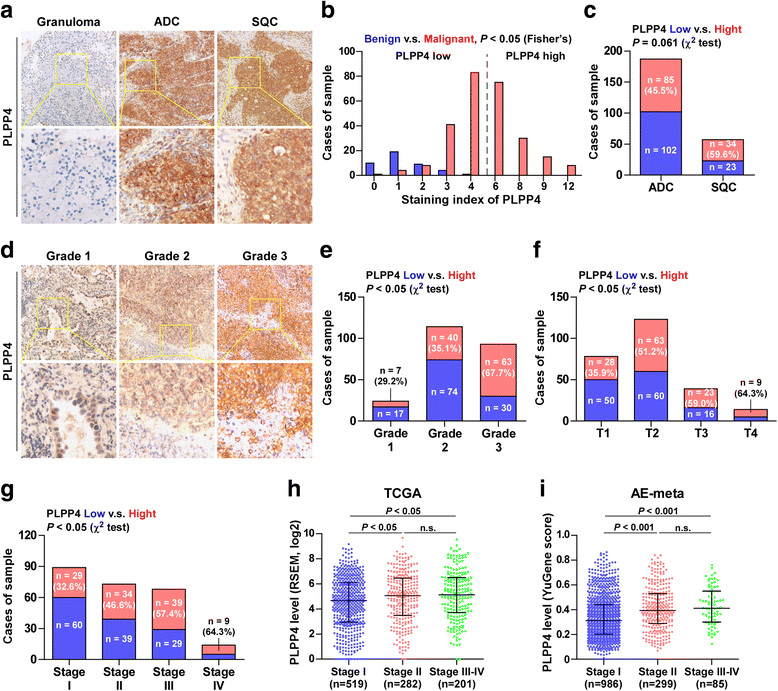
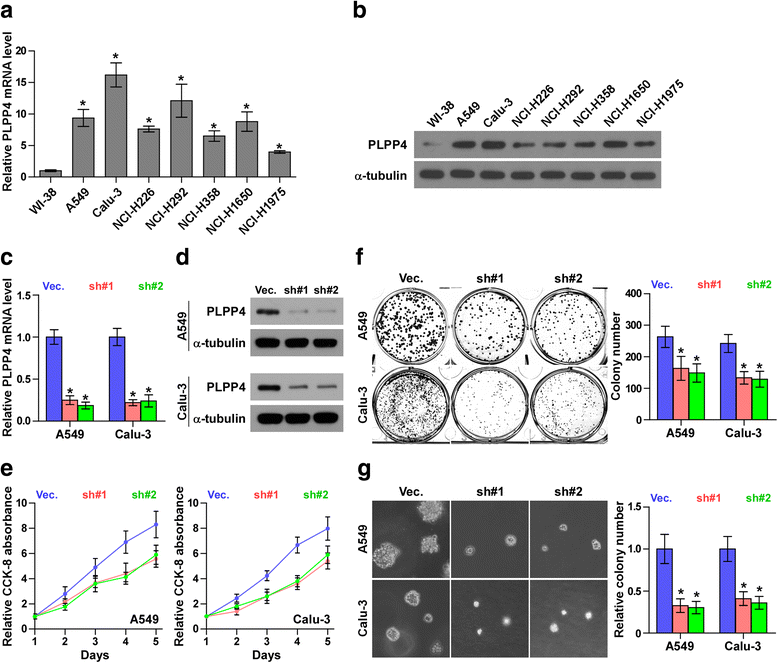
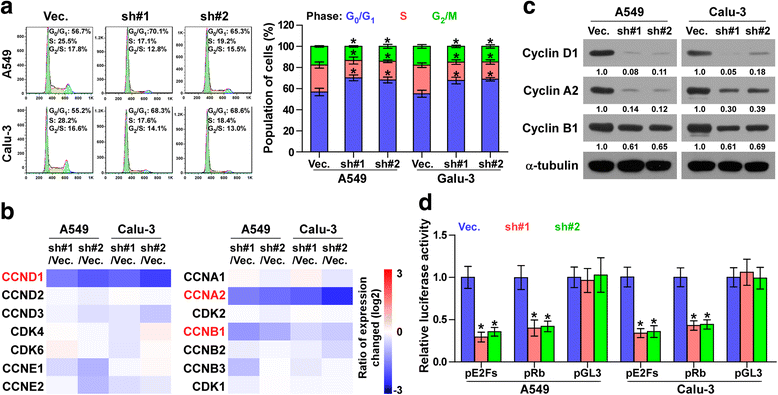
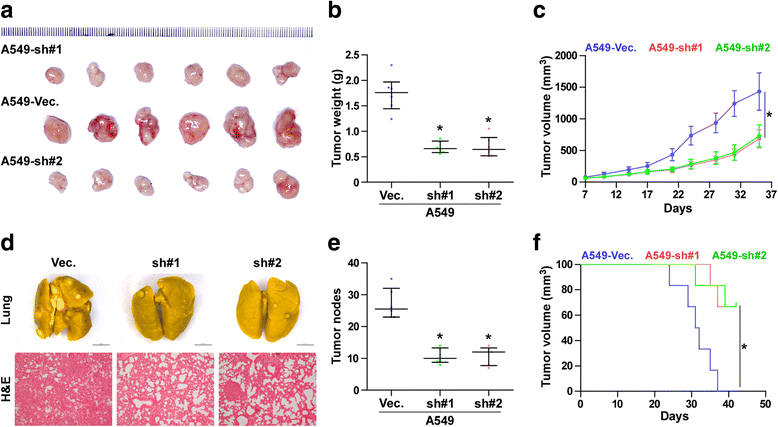
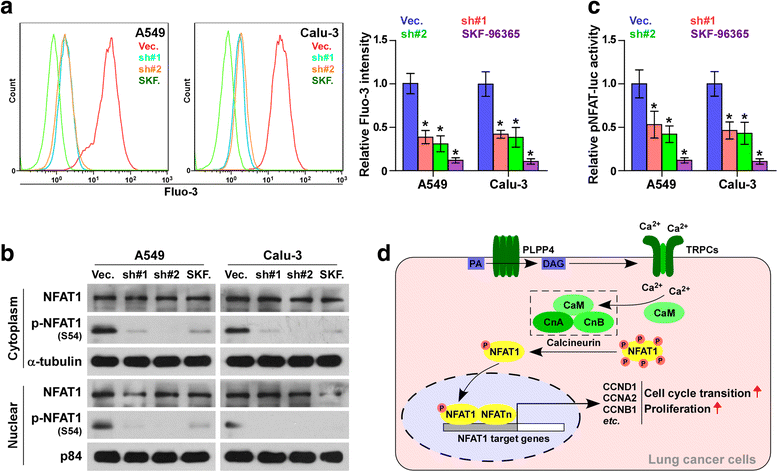
Results: PLPP4 is differentially elevated in lung adenocarcinoma (ADC) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (SQC) tissues. Statistical analysis demonstrated that high expression of PLPP4 significantly and positively correlated with clinicopathological features, including pathological grade, T category and stage, and poor overall and progression-free survival in lung carcinoma patients. Silencing PLPP4 inhibits proliferation and cell cycle progression in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo in lung carcinoma cells. Our results further reveal that PLPP4 silencing inhibits Ca2+-permeable cationic channel, suggesting that downregulation of PLPP4 inhibits proliferation and tumorigenesis in lung carcinoma cells via reducing the influx of intracellular Ca2+.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that PLPP4 may hold promise as a novel marker for the diagnosis of lung carcinoma and as a potential therapeutic target to facilitate the development of novel treatment for lung carcinoma.
Keywords: Ca2+-permeable cationic channel; Cell cycle; Lung carcinoma; PLPP4; Proliferation; Therapeutic target; Tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in compliance with the declaration of Helsinki regarding ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. The research protocols were approved by the Ethnic Committee of the Jiangmen Central Hospital, Affiliated Jiangmen Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. The ethics approval numbers of patient related experiments was 20170718A. The ethics approval statements for animal work were provided by Comments of laboratory animal ethical Committee of Guangdong Medical University. The ethics approval numbers of animal work was GDY1701033.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Gilligan D, Nicolson M, Smith I, Groen H, Dalesio O, Goldstraw P, Hatton M, Hopwood P, Manegold C, Schramel F, et al. Preoperative chemotherapy in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: results of the MRC LU22/NVALT 2/EORTC 08012 multicentre randomised trial and update of systematic review. Lancet. 2007;369:1929–1937. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60714-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

