Cholesterol metabolism and Cx43, Cx46, and Cx50 gap junction protein expression and localization in normal and diabetic and obese ob/ob and db/db mouse testes
- PMID: 28851737
- PMCID: PMC5866387
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00215.2017
Cholesterol metabolism and Cx43, Cx46, and Cx50 gap junction protein expression and localization in normal and diabetic and obese ob/ob and db/db mouse testes
Abstract
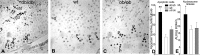
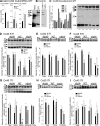
Decreased fertility and birth rates arise from metabolic disorders. This study assesses cholesterol metabolism and Cx46, Cx50, and Cx43 expression in interstitium- and seminiferous tubule-enriched fractions of leptin-deficient ( ob/ob) and leptin receptor-deficient ( db/db) mice, two type 2 diabetes and obesity models associated with infertility. Testosterone levels decreased and glucose and free and esterified cholesterol (FC and EC) levels increased in serum, whereas FC and EC levels decreased in the interstitium, in ob/ob and db/db mice. In tubules, a decrease in EC caused FC-to-EC ratios to increase in db/db mice. In tubules, only acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyl transferase type 1 and 2 protein levels significantly decreased in ob/ob, but not db/db, mice compared with wild-type mice, and imbalances in the cholesterol transporters Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1), ATP-binding cassette A1 (ABCA1), scavenger receptor class B member I (SR-BI), and cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) were observed in ob/ob and db/db mice. In tubules, 14-kDa Cx46 prevailed during development, 48- to 49- and 68- to 71-kDa Cx46 prevailed during adulthood, and total Cx46 changed little. Compared with wild-type mice, 14-kDa Cx46 increased, whereas 48- to 49- and 68- to 71-kDa Cx46 decreased, in tubules, whereas the opposite occurred in the interstitium, in db/db and ob/ob mice. Total and 51-kDa Cx50 increased in db/db and ob/ob interstitium and tubules. Cx43 levels decreased in ob/ob interstitium and tubules, whereas Cx43 decreased in db/db interstitium but increased in db/db tubules. Apoptosis levels measured by ELISA and numbers of apostain-labeled apoptotic cells significantly increased in db/db, but not ob/ob, tubules. Testicular db/db capillaries were Cx50-positive but weakly Cx43-positive with a thickened lamina, suggesting altered permeability. Our findings indicate that the db mutation-induced impairment of meiosis may arise from imbalances in cholesterol metabolism and upregulated Cx43 expression and phosphorylation in tubules.
Keywords: Sertoli cell; cholesterol; meiosis; spermatogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Akpovi CD, Anago EAA, Segbo JAG, Manindji C, Medehouenou TCM, Loko F, Vitale ML, Pelletier R-M. Blood biochemical parameter levels vary with spermatogenesis in seasonal reproductive model, the mink (Mustela vison). Int J Biosci 6: 222–229, 2015. doi: 10.12692/ijb/6.2.222-229. - DOI
-
- Akpovi CD, Pelletier R-M. A revised and improved method for the isolation of seminiferous tubule-enriched fractions that preserves the phosphorylated and glycosylated forms of proteins. In: Human Embryogenesis: Methods and Protocols, edited by Lafond J, Vaillancourt C. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Springer Protocols, 2009, p. 159–168. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-009-0_9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

