TFG facilitates outer coat disassembly on COPII transport carriers to promote tethering and fusion with ER-Golgi intermediate compartments
- PMID: 28851831
- PMCID: PMC5604033
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1709120114
TFG facilitates outer coat disassembly on COPII transport carriers to promote tethering and fusion with ER-Golgi intermediate compartments
Erratum in
-
Correction for Hanna et al., TFG facilitates outer coat disassembly on COPII transport carriers to promote tethering and fusion with ER-Golgi intermediate compartments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 3;114(40):E8547-E8548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715867114. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28973870 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
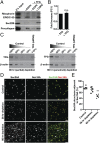
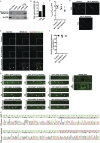
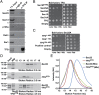
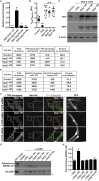
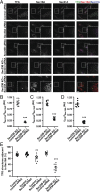
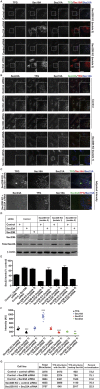
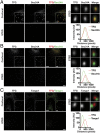
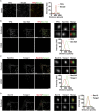
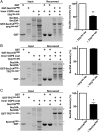
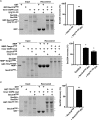
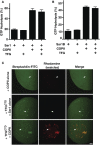
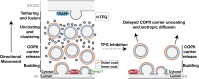
The conserved coat protein complex II (COPII) mediates the initial steps of secretory protein trafficking by assembling onto subdomains of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in two layers to generate cargo-laden transport carriers that ultimately fuse with an adjacent ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). Here, we demonstrate that Trk-fused gene (TFG) binds directly to the inner layer of the COPII coat. Specifically, the TFG C terminus interacts with Sec23 through a shared interface with the outer COPII coat and the cargo receptor Tango1/cTAGE5. Our findings indicate that TFG binding to Sec23 outcompetes these other associations in a concentration-dependent manner and ultimately promotes outer coat dissociation. Additionally, we demonstrate that TFG tethers vesicles harboring the inner COPII coat, which contributes to their clustering between the ER and ERGIC in cells. Together, our studies define a mechanism by which COPII transport carriers are retained locally at the ER/ERGIC interface after outer coat disassembly, which is a prerequisite for fusion with ERGIC membranes.
Keywords: COPII; Trk-fused gene; coat disassembly; endoplasmic reticulum; tether.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TFG clusters COPII-coated transport carriers and promotes early secretory pathway organization.EMBO J. 2015 Mar 12;34(6):811-27. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489032. Epub 2015 Jan 13. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25586378 Free PMC article.
-
COPII-mediated trafficking at the ER/ERGIC interface.Traffic. 2019 Jul;20(7):491-503. doi: 10.1111/tra.12654. Epub 2019 May 30. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 31059169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vesicle-mediated export from the ER: COPII coat function and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1833(11):2464-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23419775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TFG regulates inner COPII coat recruitment to facilitate anterograde secretory protein transport.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Aug 1;35(8):ar113. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-06-0282. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38985515 Free PMC article.
-
The highly conserved COPII coat complex sorts cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum and targets it to the golgi.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a013367. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013367. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378591 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-Associated Factors at the Endoplasmic Reticulum-Golgi Interface.Traffic. 2025 Jan-Mar;26(1-3):e70001. doi: 10.1111/tra.70001. Traffic. 2025. PMID: 40047103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 1;23(3):1697. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031697. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncanonical autophagy at ER exit sites regulates procollagen turnover.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 23;115(43):E10099-E10108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1814552115. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30287488 Free PMC article.
-
TRK-fused gene (TFG) regulates ULK1 stability via TRAF3-mediated ubiquitination and protects macrophages from LPS-induced pyroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jan 28;13(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04539-9. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35091545 Free PMC article.
-
R106C TFG variant causes infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy "plus" syndrome.Neurogenetics. 2018 Aug;19(3):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s10048-018-0552-x. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Neurogenetics. 2018. PMID: 29971521
References
-
- Venditti R, Wilson C, De Matteis MA. Exiting the ER: What we know and what we don’t. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C, Hauri H-P. The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): In search of its identity and function. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2173–2183. - PubMed
-
- Martínez-Menárguez JA, Geuze HJ, Slot JW, Klumperman J. Vesicular tubular clusters between the ER and Golgi mediate concentration of soluble secretory proteins by exclusion from COPI-coated vesicles. Cell. 1999;98:81–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

