Fluoroquinolone structure and translocation flux across bacterial membrane
- PMID: 28851902
- PMCID: PMC5575017
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-08775-4
Fluoroquinolone structure and translocation flux across bacterial membrane
Abstract
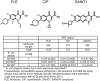
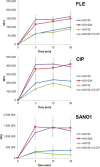
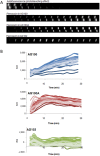
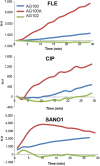
Bacterial multidrug resistance is a worrying health issue. In Gram-negative antibacterial research, the challenge is to define the antibiotic permeation across the membranes. Passing through the membrane barrier to reach the inhibitory concentration inside the bacterium is a pivotal step for antibacterial molecules. A spectrofluorimetric methodology has been developed to detect fluoroquinolones in bacterial population and inside individual Gram-negative bacterial cells. In this work, we studied the antibiotic accumulation in cells expressing various levels of efflux pumps. The assays allow us to determine the intracellular concentration of the fluoroquinolones to study the relationships between the level of efflux activity and the antibiotic accumulation, and finally to evaluate the impact of fluoroquinolone structures in this process. This represents the first protocol to identify some structural parameters involved in antibiotic translocation and accumulation, and to illustrate the recently proposed "Structure Intracellular Concentration Activity Relationship" (SICAR) concept.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors (M.M., E.B.) declare competing financial interests: M.M. and E.B. are current employees of SANOFI R&D.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

