Enhanced Fluorine-19 MRI Sensitivity using a Cryogenic Radiofrequency Probe: Technical Developments and Ex Vivo Demonstration in a Mouse Model of Neuroinflammation
- PMID: 28851959
- PMCID: PMC5575026
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09622-2
Enhanced Fluorine-19 MRI Sensitivity using a Cryogenic Radiofrequency Probe: Technical Developments and Ex Vivo Demonstration in a Mouse Model of Neuroinflammation
Abstract
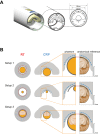
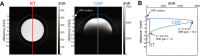
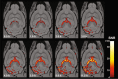
Neuroinflammation can be monitored using fluorine-19 (19F)-containing nanoparticles and 19F MRI. Previously we studied neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) using room temperature (RT) 19F radiofrequency (RF) coils and low spatial resolution 19F MRI to overcome constraints in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This yielded an approximate localization of inflammatory lesions. Here we used a new 19F transceive cryogenic quadrature RF probe ( 19 F-CRP) that provides the SNR necessary to acquire superior spatially-resolved 19F MRI. First we characterized the signal-transmission profile of the 19 F-CRP. The 19 F-CRP was then benchmarked against a RT 19F/1H RF coil. For SNR comparison we used reference compounds including 19F-nanoparticles and ex vivo brains from EAE mice administered with 19F-nanoparticles. The transmit/receive profile of the 19 F-CRP diminished with increasing distance from the surface. This was counterbalanced by a substantial SNR gain compared to the RT coil. Intraparenchymal inflammation in the ex vivo EAE brains was more sharply defined when using 150 μm isotropic resolution with the 19 F-CRP, and reflected the known distribution of EAE histopathology. At this spatial resolution, most 19F signals were undetectable using the RT coil. The 19 F-CRP is a valuable tool that will allow us to study neuroinflammation with greater detail in future in vivo studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fluorine-19 MRI at 21.1 T: enhanced spin-lattice relaxation of perfluoro-15-crown-5-ether and sensitivity as demonstrated in ex vivo murine neuroinflammation.MAGMA. 2019 Feb;32(1):37-49. doi: 10.1007/s10334-018-0710-z. Epub 2018 Nov 12. MAGMA. 2019. PMID: 30421250 Free PMC article.
-
B1 inhomogeneity correction of RARE MRI at low SNR: Quantitative in vivo 19 F MRI of mouse neuroinflammation with a cryogenically-cooled transceive surface radiofrequency probe.Magn Reson Med. 2022 Apr;87(4):1952-1970. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29094. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Magn Reson Med. 2022. PMID: 34812528
-
In vivo detection of teriflunomide-derived fluorine signal during neuroinflammation using fluorine MR spectroscopy.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(6):2490-2504. doi: 10.7150/thno.47130. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33456555 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of compressed sensing for fluorine-19 magnetic resonance imaging at low signal-to-noise ratio conditions.Magn Reson Med. 2020 Aug;84(2):592-608. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28135. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Magn Reson Med. 2020. PMID: 31863516
-
18F-VC701-PET and MRI in the in vivo neuroinflammation assessment of a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Feb 5;15(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1044-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29402285 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quantitative 19F MRI of perfluoro-15-crown-5-ether using uniformity correction of the spin excitation and signal reception.MAGMA. 2019 Feb;32(1):25-36. doi: 10.1007/s10334-018-0696-6. Epub 2018 Aug 10. MAGMA. 2019. PMID: 30097741
-
Opportunities for Molecular Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Management: Linking Probe to Treatment.Radiology. 2022 Jun;303(3):486-497. doi: 10.1148/radiol.211252. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 35471110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorine (19F) MRI for Assessing Inflammatory Cells in the Kidney: Experimental Protocol.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2216:495-507. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0978-1_30. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33476020 Free PMC article.
-
Hardware Considerations for Preclinical Magnetic Resonance of the Kidney.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2216:131-155. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0978-1_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33475998 Free PMC article.
-
Inducing Defects in 19F-Nanocrystals Provides Paramagnetic-free Relaxation Enhancement for Improved In Vivo Hotspot MRI.Nano Lett. 2020 Oct 14;20(10):7207-7212. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02549. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Nano Lett. 2020. PMID: 32897716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilmore CP, et al. Regional variations in the extent and pattern of grey matter demyelination in multiple sclerosis: a comparison between the cerebral cortex, cerebellar cortex, deep grey matter nuclei and the spinal cord. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2009;80:182–187. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2008.148767. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

