New insights into tenocyte-immune cell interplay in an in vitro model of inflammation
- PMID: 28851983
- PMCID: PMC5575127
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09875-x
New insights into tenocyte-immune cell interplay in an in vitro model of inflammation
Abstract
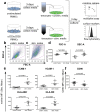
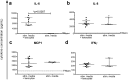
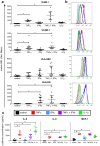
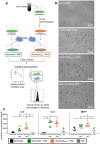
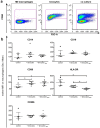
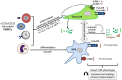
Inflammation plays an important role in the development and resolution of tendon diseases, but underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. We therefore aimed to analyze the response of human tenocytes to inflammatory stimuli and to uncover their interplay with macrophages in vitro. Tenocytes from human ruptured supraspinatus tendons (n = 10) were treated for three days with a stimulation mixture derived from activated mononuclear cells isolated from healthy human peripheral blood. Significantly increased expression levels of selected adhesion- and human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-molecules, and enhanced interleukin (IL)-6 release were detected by flow cytometry. Tenocyte stimulation with the pro-inflammatory cytokines interferon gamma, tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-1ß triggered similar changes in surface markers and enhanced the release of IL-6, IL-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In co-cultures of macrophages with pre-stimulated tenocytes, macrophages significantly increased CD80 expression, but simultaneously decreased HLA-DR-expression, which are both typical pro-inflammatory polarization markers. Co-cultures also released more IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 than tenocyte-cultures alone. We demonstrate that tenocytes respond to inflammatory environments in vitro with altered surface marker and cytokine profiles and influence macrophage polarization. Importantly, all changes detected in direct co-cultures were also present in a transwell setting, implicating that communication between the cells involves soluble factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Boileau P, et al. Arthroscopic repair of full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal? The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2005;87:1229–1240. - PubMed
-
- Kelly BA, Proffen BL, Haslauer CM, Murray MM. Platelets and plasma stimulate sheep rotator cuff tendon tenocytes when cultured in an extracellular matrix scaffold. Journal of orthopaedic research: official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2016;34:623–629. doi: 10.1002/jor.23058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

