A time series transcriptome analysis of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) varieties challenged with Ugandan cassava brown streak virus
- PMID: 28852026
- PMCID: PMC5575035
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09617-z
A time series transcriptome analysis of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) varieties challenged with Ugandan cassava brown streak virus
Abstract
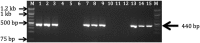
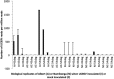
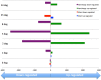
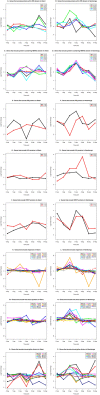
A time-course transcriptome analysis of two cassava varieties that are either resistant or susceptible to cassava brown streak disease (CBSD) was conducted using RNASeq, after graft inoculation with Ugandan cassava brown streak virus (UCBSV). From approximately 1.92 billion short reads, the largest number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was obtained in the resistant (Namikonga) variety at 2 days after grafting (dag) (3887 DEGs) and 5 dag (4911 DEGs). At the same time points, several defense response genes (encoding LRR-containing, NBARC-containing, pathogenesis-related, late embryogenesis abundant, selected transcription factors, chaperones, and heat shock proteins) were highly expressed in Namikonga. Also, defense-related GO terms of 'translational elongation', 'translation factor activity', 'ribosomal subunit' and 'phosphorelay signal transduction', were overrepresented in Namikonga at these time points. More reads corresponding to UCBSV sequences were recovered from the susceptible variety (Albert) (733 and 1660 read counts per million (cpm)) at 45 dag and 54 dag compared to Namikonga (10 and 117 cpm respectively). These findings suggest that Namikonga's resistance involves restriction of multiplication of UCBSV within the host. These findings can be used with other sources of evidence to identify candidate genes and biomarkers that would contribute substantially to knowledge-based resistance breeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Storey HH. Virus diseases of East African plants. VI-A progress report on studies of the disease of cassava. E Afri Agric J. 1936;2:34–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

