TCA cycle rewiring fosters metabolic adaptation to oxygen restriction in skeletal muscle from rodents and humans
- PMID: 28852047
- PMCID: PMC5575144
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-10097-4
TCA cycle rewiring fosters metabolic adaptation to oxygen restriction in skeletal muscle from rodents and humans
Abstract
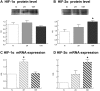
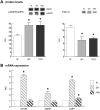
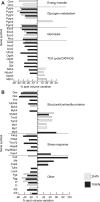
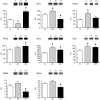
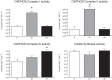
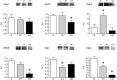
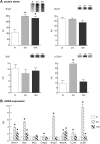
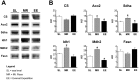
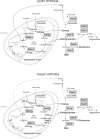
In mammals, hypoxic stress management is under the control of the Hypoxia Inducible Factors, whose activity depends on the stabilization of their labile α subunit. In particular, the skeletal muscle appears to be able to react to changes in substrates and O2 delivery by tuning its metabolism. The present study provides a comprehensive overview of skeletal muscle metabolic adaptation to hypoxia in mice and in human subjects exposed for 7/9 and 19 days to high altitude levels. The investigation was carried out combining proteomics, qRT-PCR mRNA transcripts analysis, and enzyme activities assessment in rodents, and protein detection by antigen antibody reactions in humans and rodents. Results indicate that the skeletal muscle react to a decreased O2 delivery by rewiring the TCA cycle. The first TCA rewiring occurs in mice in 2-day hypoxia and is mediated by cytosolic malate whereas in 10-day hypoxia the rewiring is mediated by Idh1 and Fasn, supported by glutamine and HIF-2α increments. The combination of these specific anaplerotic steps can support energy demand despite HIFs degradation. These results were confirmed in human subjects, demonstrating that the TCA double rewiring represents an essential factor for the maintenance of muscle homeostasis during adaptation to hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

