Assessment of the Efficacy and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid Gel Injection in the Restoration of Fullness of the Upper Lips
- PMID: 28852297
- PMCID: PMC5561704
- DOI: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_115_16
Assessment of the Efficacy and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid Gel Injection in the Restoration of Fullness of the Upper Lips
Abstract
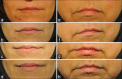
Background and aim: Lips have a significant role in face aesthetic perception, and lip augmentation is one of the most commonly requested aesthetic procedures. Non-permanent dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid (HA), are used for augmenting the lips. This article presents the results of Phase II, before - after designed study, assessing the safety and efficacy of a soft tissue HA filler, for upper lip augmentation.
Materials and methods: Investigators treated 10 healthy adult women 28-45 years old, using a single injection of Hyamax Kiss soft tissue HA filler (a product from Hyamed Laboratories, Switzerland) for upper lip augmentation. The primary efficacy endpoint was an increase in lip fullness at least one grade on Medicis Lip Fullness Scale at 2, 12 and 24 weeks post-treatment. Furthermore, the effectiveness and durability of filler were assessed using a 5-point Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA). Adverse events and volunteers' satisfaction were reported using visual analog scale.
Results: Response to treatment (as defined above) after 2, 12 and 24 weeks were observed in 80%, 70% and 80% of patients, respectively. No statistical difference was found in response to treatment rate between follow-up visits (P = 0.83). The mean value of IGA score in weeks 2, 12 and 24 were 3.4 ± 0.96, 3.3 ± 0.67 and 3.3 ± 0.67, respectively. The study subjects were almost all satisfied with their lip improvement. Reported adverse effects were temporary and mostly mild in severity.
Conclusion: Soft tissue HA filler tested in this study was well tolerated, efficient and durable when used for upper lip augmentation.
Keywords: Hyaluronic acid; lip augmentation; lip filler.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nestor MS. Hyaluronic acid fillers. In: Draelos ZD, editor. Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and Procedures. 2nd ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: Blackwell; 2010. pp. 352–5.
-
- Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Soft tissue augmentation. In: Bolognia J, editor. Text Book of Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2012. pp. 2547–60.
-
- Niamtu J., 3rd New lip and wrinkle fillers. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2005;17:17–28, v. - PubMed
-
- Klein AW. In search of the perfect lip: 2005. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:1599–603. - PubMed
-
- Bisson M, Grobbelaar A. The esthetic properties of lips: A comparison of models and nonmodels. Angle Orthod. 2004;74:162–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

