Branched-chain amino acids and muscle protein synthesis in humans: myth or reality?
- PMID: 28852372
- PMCID: PMC5568273
- DOI: 10.1186/s12970-017-0184-9
Branched-chain amino acids and muscle protein synthesis in humans: myth or reality?
Abstract
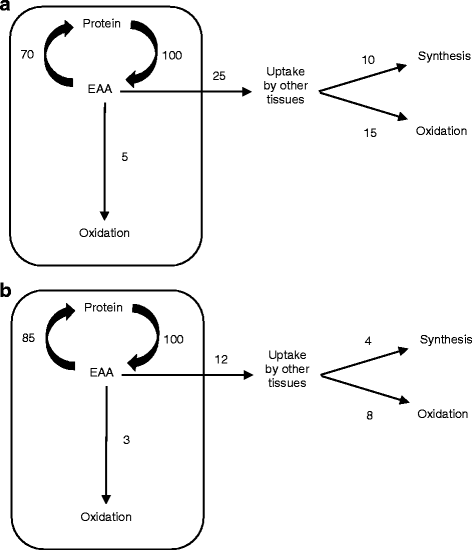
The branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) are leucine, valine and isoleucine. A multi-million dollar industry of nutritional supplements has grown around the concept that dietary supplements of BCAAs alone produce an anabolic response in humans driven by a stimulation of muscle protein synthesis. In this brief review the theoretical and empirical bases for that claim are discussed. Theoretically, the maximal stimulation of muscle protein synthesis in the post-absorptive state in response to BCAAs alone is the difference between muscle protein breakdown and muscle protein synthesis (about 30% greater than synthesis), because the other EAAs required for synthesis of new protein can only be derived from muscle protein breakdown. Realistically, a maximal increase in muscle protein synthesis of 30% is an over-estimate because the obligatory oxidation of EAAs can never be completely suppressed. An extensive search of the literature has revealed no studies in human subjects in which the response of muscle protein synthesis to orally-ingested BCAAs alone was quantified, and only two studies in which the effect of intravenously infused BCAAs alone was assessed. Both of these intravenous infusion studies found that BCAAs decreased muscle protein synthesis as well as protein breakdown, meaning a decrease in muscle protein turnover. The catabolic state in which the rate of muscle protein breakdown exceeded the rate of muscle protein synthesis persisted during BCAA infusion. We conclude that the claim that consumption of dietary BCAAs stimulates muscle protein synthesis or produces an anabolic response in human subjects is unwarranted.
Keywords: Anabolic response; Humans; Isoleucine; Leucine; Valine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
Dr. Wolfe has received research grants and/or honoraria from the National Cattleman’s Beef Checkoff program Abbott Nutrition, Danone and PepsiCo. Dr. Wolfe owns shares in Essential Blends, LLC, and has been a consultant for Axcella LLC.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Blomstrand E, Eliasson J, Karlsson HKR, Kohnke R. Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise. J Nutr. 2006;136:269S–273S. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi H, Kato H, Hirabayashi Y, Murakami H, Suzuki H. Modulations of muscle protein metabolism by branched-chain amino acids in normal and muscle-atrophying rats. J Nutr. 2006;136:234S–236S. - PubMed
-
- Waterlow JC, PJ Garlick, DJ Millward. Protein turnover in mamlian tissues and the whole body. North Holland Publishing Company. Amsterdam, 1978, p661.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
