Recovery of sympathetic nerve function after lumbar sympathectomy is slower in the hind limbs than in the torso
- PMID: 28852403
- PMCID: PMC5558500
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.211200
Recovery of sympathetic nerve function after lumbar sympathectomy is slower in the hind limbs than in the torso
Abstract
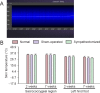
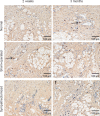
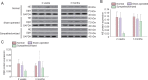
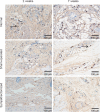
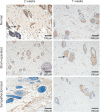
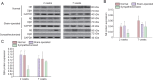
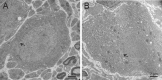
Local sympathetic denervation by surgical sympathectomy is used in the treatment of lower limb ulcers and ischemia, but the restoration of cutaneous sympathetic nerve functions is less clear. This study aims to explore the recovery of cutaneous sympathetic functions after bilateral L2-4 sympathectomy. The skin temperature of the left feet, using a point monitoring thermometer, increased intraoperatively after sympathectomy. The cytoplasm of sympathetic neurons contained tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase, visualized by immunofluorescence, indicated the accuracy of sympathectomy. Iodine starch test results suggested that the sweating function of the hind feet plantar skin decreased 2 and 7 weeks after lumbar sympathectomy but had recovered by 3 months. Immunofluorescence and western blot assay results revealed that norepinephrine and dopamine β-hydroxylase expression in the skin from the sacrococcygeal region and hind feet decreased in the sympathectomized group at 2 weeks. Transmission electron microscopy results showed that perinuclear space and axon demyelination in sympathetic cells in the L5 sympathetic trunks were found in the sympathectomized group 3 months after sympathectomy. Although sympathetic denervation occurred in the sacrococcygeal region and hind feet skin 2 weeks after lumbar sympathectomy, the skin functions recovered gradually over 7 weeks to 3 months. In conclusion, sympathetic functional recovery may account for the recurrence of hyperhidrosis after sympathectomy and the normalization of sympathetic nerve trunks after incomplete injury. The recovery of sympathetic nerve function was slower in the limbs than in the torso after bilateral L2-4 sympathectomy.
Keywords: lumbar sympathectomy; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; recovery of function; skin; sympathetic nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lumbar sympathectomy reduces vascular permeability, possibly through decreased adenosine receptor A2a expression in the hind plantar skin of rats.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018;68(1):5-15. doi: 10.3233/CH-160214. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018. PMID: 29439317
-
Sensory innervation of the dorsal portion of the lumbar intervertebral discs in rats.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001 Apr 15;26(8):946-50. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200104150-00020. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. PMID: 11317119
-
Surgical Lumbar Sympathectomy in Mice.J Vis Exp. 2024 Jul 5;(209). doi: 10.3791/66821. J Vis Exp. 2024. PMID: 39037251
-
[Lumbar sympathectomy literature review over the past 15 years].Rozhl Chir. 2016 Mar;95(3):101-6. Rozhl Chir. 2016. PMID: 27091617 Review. Czech.
-
Management of Plantar Hyperhidrosis with Endoscopic Lumbar Sympathectomy.Thorac Surg Clin. 2016 Nov;26(4):465-469. doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2016.06.012. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Thorac Surg Clin. 2016. PMID: 27692206 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of T2-T4 sympathicotomy in skin temperature of pediatric patients with hyperhidrosis: a thermographic follow-up.Clin Auton Res. 2024 Jun;34(3):379-382. doi: 10.1007/s10286-024-01047-y. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Clin Auton Res. 2024. PMID: 38913299 No abstract available.
-
Advances in Clinical Outcomes of Endoscopic Lumbar Sympathectomy: Analysis of 494 Consecutive Patients at a Single Institution.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 17;14(12):4311. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124311. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40566053 Free PMC article.
-
Lumbar Sympathetic Trunk Injury: An Underestimated Complication of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion.Orthop Surg. 2023 Apr;15(4):1053-1059. doi: 10.1111/os.13692. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Orthop Surg. 2023. PMID: 36855251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buche M, Randour P, Mayne A, Joucken K, Schoevaerdts JC. Neuralgia following lumbar sympathectomy. Ann Vasc Surg. 1988;2:279–281. - PubMed
-
- Coveliers HM, Hoexum F, Nederhoed JH, Wisselink W, Rauwerda JA. Thoracic sympathectomy for digital ischemia: a summary of evidence. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:273–277. - PubMed
-
- Dellon AL, Hoke A, Williams EH, Williams CG, Zhang Z, Rosson GD. The sympathetic innervation of the human foot. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:905–909. - PubMed
-
- Donadio V, Nolano M, Provitera V, Stancanelli A, Lullo F, Liguori R, Santoro L. Skin sympathetic adrenergic innervation: an immunofluorescence confocal study. Ann Neurol. 2006;59:376–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

