Metagenomic mining pectinolytic microbes and enzymes from an apple pomace-adapted compost microbial community
- PMID: 28852421
- PMCID: PMC5568718
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-017-0885-y
Metagenomic mining pectinolytic microbes and enzymes from an apple pomace-adapted compost microbial community
Abstract
Background: Degradation of pectin in lignocellulosic materials is one of the key steps for biofuel production. Biological hydrolysis of pectin, i.e., degradation by pectinolytic microbes and enzymes, is an attractive paradigm because of its obvious advantages, such as environmentally friendly procedures, low in energy demand for lignin removal, and the possibility to be integrated in consolidated process. In this study, a metagenomics sequence-guided strategy coupled with enrichment culture technique was used to facilitate targeted discovery of pectinolytic microbes and enzymes. An apple pomace-adapted compost (APAC) habitat was constructed to boost the enrichment of pectinolytic microorganisms.
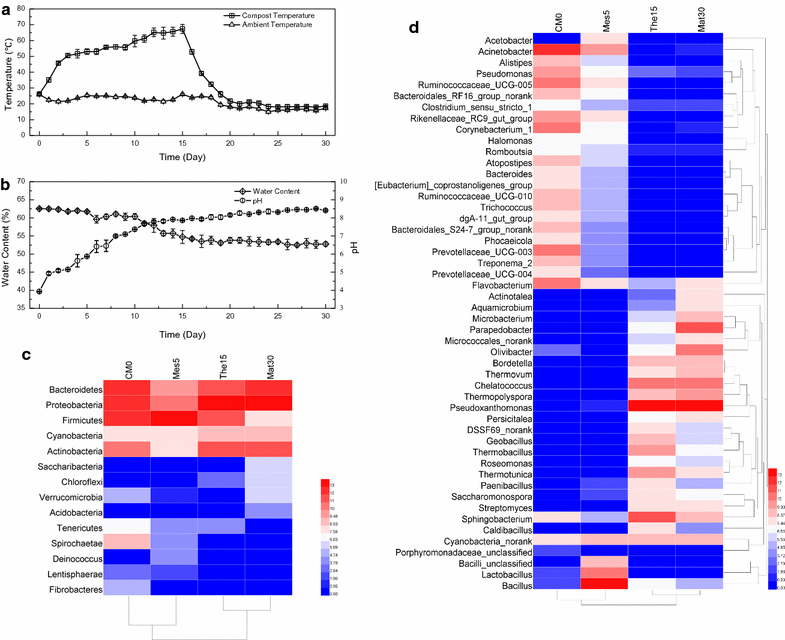
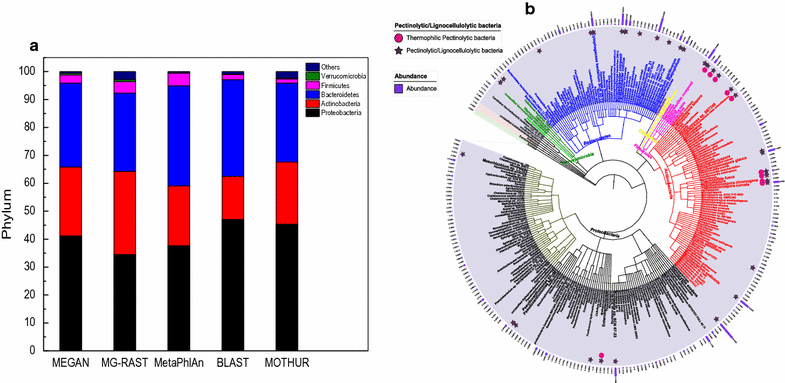
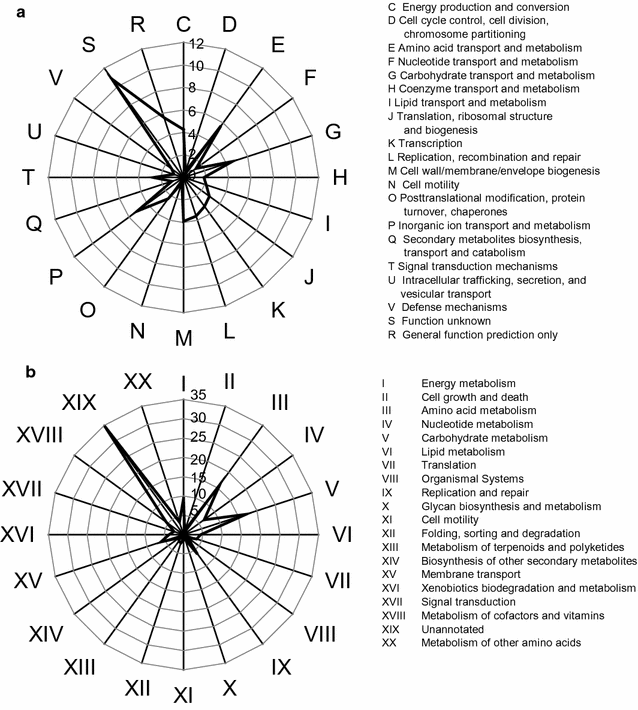
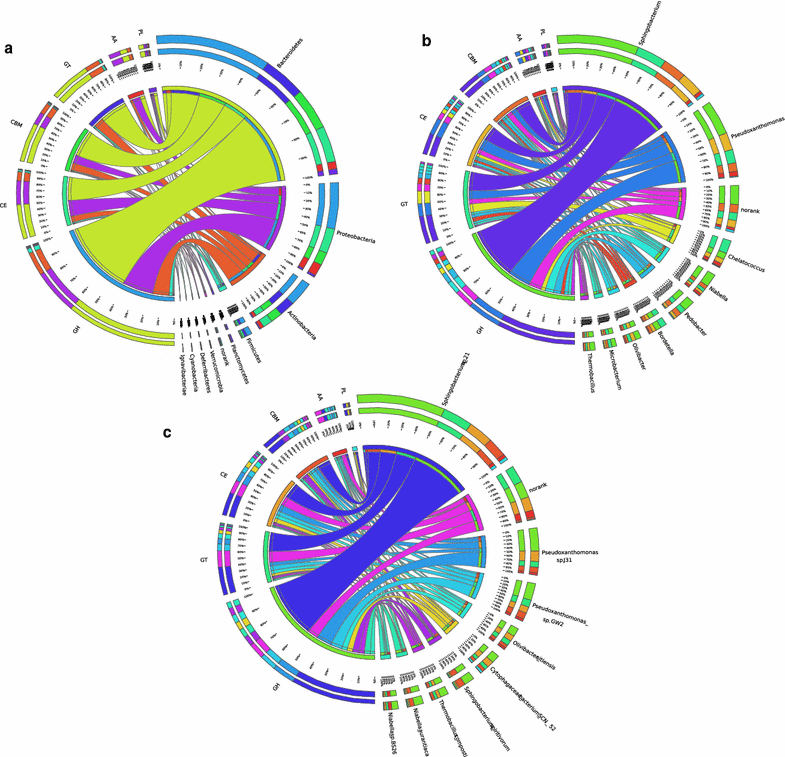
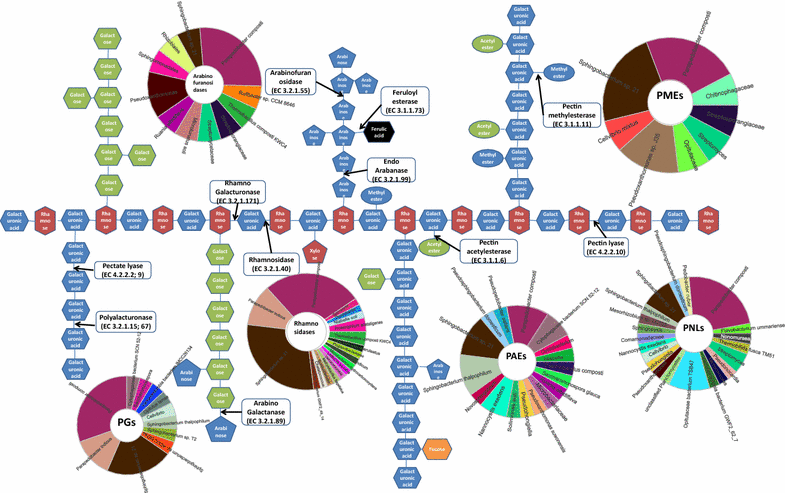
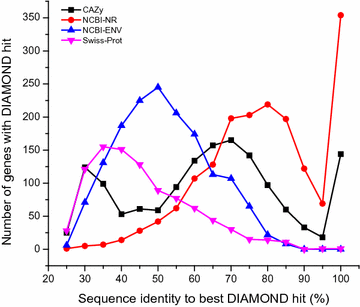
Results: Analyses of 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing revealed that microbial communities changed dramatically during composting with some bacterial populations being greatly enriched. Metagenomics data showed that apple pomace-adapted compost microbial community (APACMC) was dominated by Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes. Functional analysis and carbohydrate-active enzyme profiles confirmed that APACMC had been successfully enriched for the targeted functions. Among the 1756 putative genes encoding pectinolytic enzymes, 129 were predicted as novel (with an identity <30% to any CAZy database entry) and only 1.92% were more than 75% identical with proteins in NCBI environmental database, demonstrating that they have not been observed in previous metagenome projects. Phylogenetic analysis showed that APACMC harbored a broad range of pectinolytic bacteria and many of them were previously unrecognized.
Conclusions: The immensely diverse pectinolytic microbes and enzymes found in our study will expand the arsenal of proficient degraders and enzymes for lignocellulosic biofuel production. Our study provides a powerful approach for targeted mining microbes and enzymes in numerous industries.
Keywords: Compost habitat; Lignocellulosic biofuel; Metagenomic; Pectin; Pectinolytic microbes and enzymes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 29;12(10):1388. doi: 10.3390/biom12101388. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291597 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and sequence-based metagenomics to uncover carbohydrate-degrading enzymes from composting samples.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;107(17):5379-5401. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12627-9. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37417976 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic analysis of microbial consortia enriched from compost: new insights into the role of Actinobacteria in lignocellulose decomposition.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016 Jan 29;9:22. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0440-2. eCollection 2016. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016. PMID: 26834834 Free PMC article.
-
Lignocellulose degradation by rumen bacterial communities: New insights from metagenome analyses.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 15;229:115925. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115925. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37086884 Review.
-
Application of metagenomic techniques in mining enzymes from microbial communities for biofuel synthesis.Biotechnol Adv. 2012 Jul-Aug;30(4):920-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.01.021. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Biotechnol Adv. 2012. PMID: 22306331 Review.
Cited by
-
The purification and characterization of a novel alkali-stable pectate lyase produced by Bacillus subtilis PB1.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 3;33(10):190. doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2357-8. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28975516
-
Characterization of Novel Pectinolytic Enzymes Derived from the Efficient Lignocellulose Degradation Microbiota.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 29;12(10):1388. doi: 10.3390/biom12101388. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291597 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and sequence-based metagenomics to uncover carbohydrate-degrading enzymes from composting samples.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;107(17):5379-5401. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12627-9. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37417976 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic investigation of bacterial laccases in a straw-amended soil.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 28;13:e19327. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19327. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40313389 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal pectinases: an insight into production, innovations and applications.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 11;39(11):305. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03741-x. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37691054 Review.
References
-
- Biswal AK, Hao Z, Pattathil S, Yang X, Winkeler K, Collins C, Mohanty SS, Richardson EA, Gelineo-Albersheim I, Hunt K, Ryno D, Sykes RW, Turner GB, Ziebell A, Gjersing E, Lukowitz W, Davis MF, Decker SR, Hahn MG, Mohnen D. Downregulation of GAUT12 in Populus deltoides by RNA silencing results in reduced recalcitrance, increased growth and reduced xylan and pectin in a woody biofuel feedstock. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8:41. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0218-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswal AK, Soeno K, Gandla ML, Immerzeel P, Pattathil S, Lucenius J, Serimaa R, Hahn MG, Moritz T, Jönsson LJ. Aspen pectate lyase Ptxt PL1-27 mobilizes matrix polysaccharides from woody tissues and improves saccharification yield. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014;7(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-7-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

