The cardioprotective effect of vanillic acid on hemodynamic parameters, malondialdehyde, and infarct size in ischemia-reperfusion isolated rat heart exposed to PM10
- PMID: 28852440
- PMCID: PMC5569588
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.9007
The cardioprotective effect of vanillic acid on hemodynamic parameters, malondialdehyde, and infarct size in ischemia-reperfusion isolated rat heart exposed to PM10
Abstract
Objectives: Particulate matter (PM) exposure can promote cardiac ischemia and myocardial damage. The effects of PM10 on hemodynamic parameters, lipid peroxidation, and infarct size induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury and the protective effects of vanillic acid (VA) in isolated rat heart were investigated.
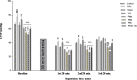
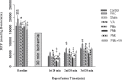
Materials and methods: Eighty male Wistar rats (250-300 g) were divided into 8 groups (n=10): Control, Sham, VAc, VA, PMa (0.5 mg/kg PM, intratracheal instillation), PMb (2.5 mg/kg PM, intratracheal instillation), PMc (5 mg/kg PM, intratracheal instillation), and PMc + VA (5 mg/kg PM, intratracheal instillation; and 10 mg/kg vanillic acid, gavage for 10 days). PM10 was instilled into the trachea in two stages, within 48 hr. After isolating the hearts and transfer to a Langendorff apparatus, hearts were subjected to 30 min ischemia and 60 min reperfusion. Hemodynamic parameters (±dp/dt, LVSP, LVDP, and RPP), production of lipid peroxidation (MDA), and infarct size were assessed.
Results: A significant decrease in ±dp/dt, LVSP, LVDP and RPP occurred in PM groups. A significant increase in MDA and myocardial infarct size occurred in PM groups. A significant increase in LVDP, LVSP, ±dp/dt, RPP and decrease in infarct size, MDA, and myocardial dysfunction was observed in groups that received vanillic acid after ischemia-reperfusion.
Conclusion: It was demonstrated that PM10 increases MDA, as well as the percentage of cardiac infarct size, and has negative effects on hemodynamic parameters. This study suggests that vanillic acid may serve as an adjunctive treatment in delaying the progression of ischemic heart disease.
Keywords: Hemodynamic parameters; Infarct size; Ischemia–reperfusion; Malondialdehyde Particulate matter; Vanillic acid.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Disturbance effects of PM₁₀ on iNOS and eNOS mRNA expression levels and antioxidant activity induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart: protective role of vanillic acid.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Mar;23(6):5154-65. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5759-x. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26552794
-
The effects of PM10 on electrocardiogram parameters, blood pressure and oxidative stress in healthy rats: the protective effects of vanillic acid.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Oct;23(19):19551-60. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7168-1. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27392621
-
Effect of vanillic acid on ischemia-reperfusion of isolated rat heart: Hemodynamic parameters and infarct size assays.Indian J Exp Biol. 2015 Oct;53(10):641-6. Indian J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26665294
-
Effects of gallic acid on hemodynamic parameters and infarct size after ischemia-reperfusion in isolated rat hearts with alloxan-induced diabetes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:612-618. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.014. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 29035826
-
Gallic acid protects particulate matter (PM10) triggers cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation causing heart adverse events in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jun;26(18):18200-18207. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05223-w. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31041709
Cited by
-
From smog to scarred hearts: unmasking the detrimental impact of air pollution on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jan 31;82(1):65. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05585-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39888395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Trimetazidine on QT-interval Prolongation and Cardiac Hypertrophy in Diabetic Rats.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019 Feb;112(2):173-178. doi: 10.5935/abc.20180248. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30570065 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Effect and Mechanism of Rhizoma Corydalis on Myocardial Infarction Through an Integrated Network Pharmacology Approach and Experimental Verification.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 22;13:927488. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.927488. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35935870 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic Acids of Plant Origin-A Review on Their Antioxidant Activity In Vitro (O/W Emulsion Systems) Along with Their in Vivo Health Biochemical Properties.Foods. 2020 Apr 24;9(4):534. doi: 10.3390/foods9040534. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32344540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of crocin on hemodynamic parameters, electrocardiogram parameters, and oxidative stress in isolated hearts of rats exposed to PM10.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Apr;25(4):460-467. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.61163.13533. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35656072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canbaz S, Duran E, Ege T, Sunar H, Cikirikcioglu M, Acipayam M. The effects of intracoronary administration of vitamin E on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury during coronary artery surgery. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;51:57–61. - PubMed
-
- Kinugasa Y, Ogino K, Furuse Y, Shiomi T, Tsutsui H, Yamamoto T, et al. Allopurinol improves cardiac dysfunction after ischemia-reperfusion via reduction of oxidative stress in isolated perused rat hearts. Circ J. 2003;67:781–82. - PubMed
-
- Dhalla NS, Elmoselhi AB, Hata T, Makino N. Status of myocardial antioxidants in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;47:446–456. - PubMed
-
- Cozzi E, Hazarika S, Stallings HW, 3rd, Cascio WE, Devlin RB, Lust RM, et al. Ultrafine particulate matter exposure augments ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;291:H894–903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
